You experience the advantages of PETG in demanding 3D printing projects. PETG filament provides greater flexibility and impact resistance than PLA filament. The table below shows PETG’s medium flexibility and impact resistance, with tensile strength values that meet challenging needs. PLA vs PETG performance in strength and durability proves critical for your application.
|
Property |
PLA |
PETG |
|---|---|---|
|
Tensile Strength |
40-50 MPa |
|
|
Impact Resistance |
Low |
Medium |
|
Flexibility |
Low |
Medium |
Key Takeaways
- PETG filament offers stronger, more flexible, and more durable 3D prints than PLA, making it ideal for functional parts that must withstand impacts and stress.
- PETG resists heat, water, UV light, and many chemicals better than PLA, so it performs well outdoors and in tough environments.
- While PETG requires higher printing temperatures and a heated bed, it provides excellent layer adhesion and lasting print quality for advanced projects.
Advantages of PETG

Strength
You demand reliable strength from your 3D printing materials, especially for functional parts. PETG filament delivers consistent tensile strength, making it a top choice for demanding applications. While PLA and PETG both reach similar tensile strength values in static tests, PETG stands out in real-world use. You benefit from PETG’s ability to withstand dynamic loads and impacts without shattering. PLA often fails suddenly and brittle under shock or vibration, but PETG deforms and survives these stresses.
PETG’s superior strength comes from its excellent layer adhesion and ductile failure mode. You can trust PETG to maintain integrity even when printed in challenging orientations.
Here is a comparison of key mechanical properties:
|
Mechanical Property |
PLA (MPa or kJ/m²) |
PETG (MPa or kJ/m²) |
|---|---|---|
|
Tensile Strength |
35 ± 4 |
32 ± 4 |
|
Impact Strength |
26.6 ± 2.8 |
52.7 ± 2.4 |
|
Flexural Strength |
76 ± 5 |
65 ± 4 |
You see that PETG offers high impact strength, which means your parts can handle drops, bumps, and stress without breaking. This advantage of PETG ensures your prints last longer and perform better in tough environments.
Durability
Durability matters when you need parts that last. PETG filament provides outstanding durability, resisting wear and tear over time. You notice that PETG does not become brittle or crack easily, even after repeated use. PLA, on the other hand, tends to degrade faster, especially when exposed to sunlight or moisture.
PETG’s durability also extends to its resistance to environmental factors. You benefit from PETG’s water resistance, which prevents swelling or weakening when exposed to humidity. PETG also resists UV light, so your prints stay strong and stable outdoors. PLA lacks this level of protection and may lose strength or color when left outside.
- PETG offers better water resistance, UV resistance, and chemical resistance than PLA.
- You can use PETG for outdoor projects, mechanical parts, and items exposed to harsh conditions.
- PETG’s durability means fewer failed prints and longer-lasting results.
Flexibility
Flexibility sets PETG apart from PLA. When you need parts that bend without breaking, PETG filament gives you the performance you want. PETG stretches and flexes under stress, absorbing energy instead of snapping. PLA feels rigid and strong, but it breaks suddenly when pushed too far.
Mechanical tests show PETG’s flexibility in action:
|
Property |
PLA (MPa or %) |
PETG (MPa or %) |
|---|---|---|
|
Breaking Elongation |
12.2 ± 1.8 % |
11.2 ± 0.8 % |
|
Bending Modulus |
2750 ± 160 |
1670 ± 120 |
|
Impact Strength |
26.6 ± 2.8 kJ/m² |
52.7 ± 2.4 kJ/m² |
You notice that PETG’s lower bending modulus means it bends more easily than PLA. This flexibility helps your parts survive impacts and repeated use. PETG’s superior strength and flexibility make it ideal for clips, brackets, and moving parts.
Tip: Choose PETG when you need a balance of strength, flexibility, and durability for your 3D prints.
The advantages of PETG include high impact strength, better rigidity compared to other flexible filaments, and excellent water resistance. You gain confidence knowing your PETG prints will perform reliably in a wide range of applications.
PETG vs PLA: Heat and Chemical Resistance

Heat Tolerance
When you compare petg vs pla for heat resistance, you see a clear difference. PETG maintains its shape and strength at higher temperatures, while PLA softens and deforms much sooner. This matters if you need parts that face heat, such as car components or outdoor fixtures.
|
Material |
Heat Deformation Temperature |
Recommended Maximum Use Temperature |
|---|---|---|
|
PLA |
~55°C |
<50°C |
|
PETG |
<70°C |
PETG’s glass transition temperature ranges from 75°C to 85°C, which is higher than PLA’s. Standardized heat tests show that PETG keeps its structural integrity even when exposed to elevated temperatures. PLA, on the other hand, loses mechanical stiffness and can warp or sag. You can trust PETG for applications that demand heat resistance and lasting strength.
Tip: Choose PETG for parts exposed to sunlight, warm environments, or mechanical stress. PETG vs. PLA in these conditions always favors PETG.
Chemical Resistance
You also need to consider chemical resistance when choosing between petg vs pla. PETG resists water, salt, and many household chemicals better than PLA. In laboratory tests, PETG showed only 0.3% mass change after weeks in water, while PLA changed by about 2.5%. This means PETG parts keep their shape and strength longer in wet or harsh environments.
|
Test Aspect |
PLA Filament Details |
PETG Filament Details |
|---|---|---|
|
Water, Ethanol, IPA, Vinegar, Salt, Citric acid, Ethylene glycol, Sodium hypochlorite |
Same as PLA |
|
|
Mass Change (Water) |
~2.5% after 8 weeks |
0.3% after 9 weeks |
|
Strength Loss |
Rapid with aggressive chemicals |
Minor with most chemicals, except acetone and long exposure to alcohols |
You gain an advantage with PETG for outdoor, marine, or packaging uses. PETG vs. PLA in chemical resistance shows PETG as the better choice for durability and strength in challenging environments.
Printability: PLA vs PETG
Print Settings
When you compare printability, you notice clear differences in ease of printing between PLA filament and PETG. PLA offers the highest ease of printing for most users. You can print PLA at lower temperatures, usually between 180°C and 220°C. This makes it easy to work with on almost any 3D printing setup. PETG requires higher temperatures, typically 220°C to 260°C, and a heated bed set to 70°C–90°C. These settings help PETG achieve strong layer bonding and good adhesion to the print bed.
|
Property/Characteristic |
PETG Filament |
PLA Filament (for comparison) |
|---|---|---|
|
Printing Temperature Range |
220°C to 260°C |
180°C to 220°C |
|
Heated Bed Temperature |
70°C to 90°C |
Not required or lower |
|
Bed Adhesion |
Strong, sticks well |
Good but less strong |
|
Cooling During Printing |
Minimal cooling recommended |
Cooling often used |
You benefit from PETG’s strong adhesion and impact resistance, but you may need to adjust print speed and cooling for best results. PLA vs PETG printability often comes down to your printer’s capabilities and your experience level.
Warping and Shrinkage
PLA filament stands out for its low shrinkage rate, around 0.3%, and minimal warping. This gives you good dimensional accuracy and makes PLA suitable for prototypes or high-precision parts. PETG also offers good dimensional accuracy, with shrinkage rates between 0.3% and 0.8%. Both filaments show minimal warping, but PETG’s amorphous structure helps maintain accuracy even on larger prints.
|
Material |
Shrinkage Rate |
Warping Behavior |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
PLA |
~0.3% |
Minimal warping |
Good for high-precision prints |
|
PETG |
0.3% - 0.8% |
Minimal warping |
Good dimensional accuracy |
You may find PLA easier to print, but PETG’s printability makes it a strong choice for functional parts. PLA vs PETG printability shows that both offer ease of printing and accuracy, but PETG’s durability and impact resistance give it an edge for demanding 3D printing projects. If you want a filament that is easy to print and suitable for prototypes, PLA is a great option. If you need strength and accuracy, PETG is ideal despite minor disadvantages like higher print temperatures.
Application Suitability: PETG Filament
Functional Parts
When you need parts that must perform under stress, PETG filament stands out as the best choice. You benefit from its high tensile strength, which ranges from 50 to 60 MPa. This strength means your printed parts can handle heavy loads and repeated use. PETG also offers impressive flexibility, with elongation at break above 100%. You avoid sudden breaks because PETG bends and absorbs impact. PLA, in contrast, has lower tensile strength and breaks at only 5–10% elongation.
Here is a quick comparison of key properties:
|
Property |
PETG Filament |
PLA Filament |
|---|---|---|
|
Tensile Strength (MPa) |
50–60 |
40–50 |
|
Elongation at Break (%) |
>100 |
5–10 |
|
Flexural Strength |
High |
Lower, more brittle |
You find PETG filament suitable for functional parts such as brackets, gears, and mechanical assemblies. Its strength and durability ensure your prints last longer and perform better in real-world applications. PLA works well for decorative items or prototypes, but it cannot match PETG’s performance for demanding tasks.
Outdoor Use
PETG filament excels in outdoor environments. You gain confidence knowing your parts resist UV light, moisture, and heat. PETG maintains its strength and shape up to 70°C, while PLA softens above 60°C and degrades quickly in sunlight. This makes PETG ideal for garden tools, outdoor fixtures, and automotive components.
Common uses of PETG include protective housings, signage, and equipment exposed to the elements. You avoid warping and cracking because PETG’s durability and environmental resistance keep your prints reliable. PLA remains best for indoor models or short-term use, but PETG gives you the strength and resilience needed for outdoor success.
Tip: Choose PETG filament when you need strength, flexibility, and durability for parts that must survive tough conditions.
PETG vs. PLA: Quick Comparison
Summary Table
When you compare pla vs petg, you see clear differences in performance, durability, and application. PETG offers higher quality results for demanding projects, while PLA remains a favorite for beginners and simple prints. You can use the summary table below to quickly evaluate which filament best fits your needs.
|
Metric |
PLA Filament |
PETG Filament |
|---|---|---|
|
Printing Temperature |
190-220°C |
220-260°C |
|
Heat Bed Temperature |
50-60°C |
75-90°C |
|
Tensile Modulus (MPa) |
Generally lower |
|
|
Durability |
Lower durability, brittle |
Higher durability, strong and flexible |
|
Heat Resistance |
Low |
Higher, better heat resistance |
|
Chemical Resistance |
Lower |
Higher |
|
UV Resistance |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Post-Processing Ease |
Easier (lower melting point, easier sanding and painting) |
More difficult (adhesive, careful sanding needed) |
|
Food Safety |
Food-safe but less water resistant |
FDA-approved, better water resistance |
|
Cost |
Generally more affordable |
Slightly more expensive |
|
Printing Difficulty |
Easier for beginners |
Slightly more challenging, requires heated bed |
You notice PETG’s tensile modulus averages around 1470 MPa, which means your parts will have greater strength and flexibility compared to PLA. This advantage becomes important for functional parts and outdoor use.
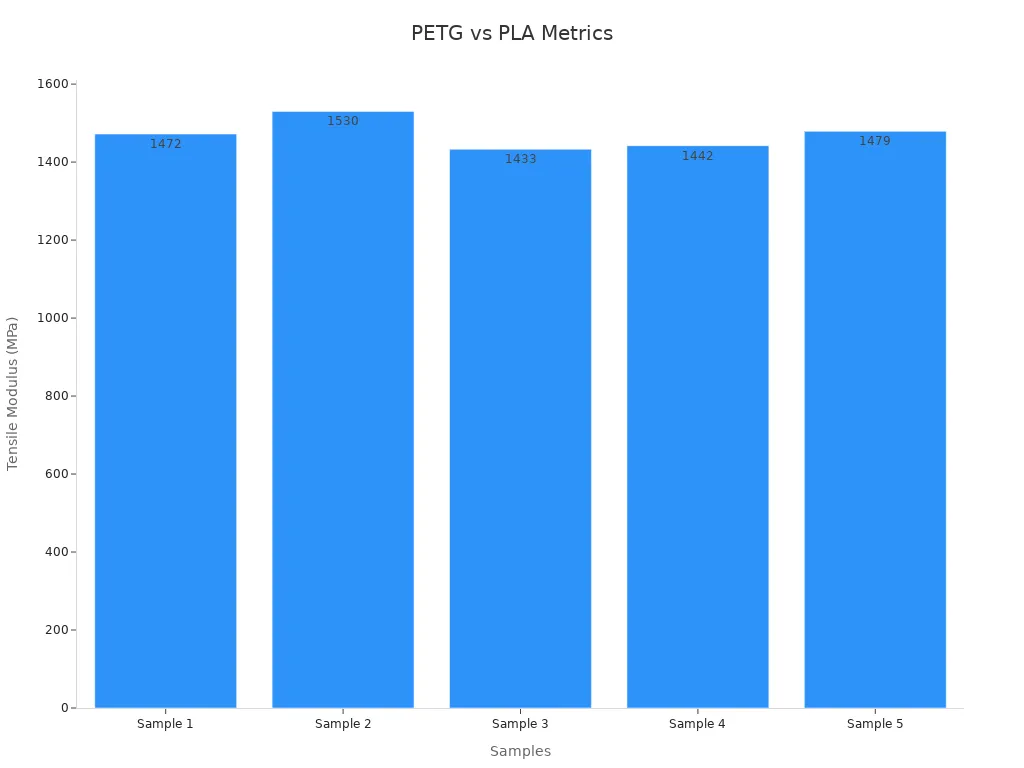
If you want a filament that prints easily and works well for decorative models, PLA is a solid choice. However, when you need parts that last longer and resist heat, chemicals, and UV light, PETG stands out in the pla vs petg debate. You gain confidence knowing PETG delivers higher quality and reliability for advanced applications.
You gain superior strength, durability, and flexibility with PETG, especially for functional or outdoor parts. PETG outperforms pla in weathering resistance and mechanical durability. Studies show PETG’s tensile strength and modulus increase outdoors, while pla weakens.
- PETG’s industrial use grows rapidly due to its reliability and chemical resistance.
FAQ
What are the main advantages of PETG filament compared to PLA filament?
You get superior strength and flexibility with PETG filament. PETG offers high impact strength, better rigidity, and greater durability than PLA filament. PETG is suitable for functional parts and outdoor use.
Is PETG filament easy to work with for 3D printing beginners?
You find PETG filament easy to work with, but PLA filament offers greater ease of printing. PETG requires higher temperatures and good adhesion, but you achieve good dimensional accuracy with proper settings.
What are common uses of PETG in 3D printing?
You use PETG filament for mechanical parts, outdoor fixtures, and applications needing water resistance. PETG is suitable for prototypes and functional parts where strength and durability matter most.



















Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.