When you ask which is faster FDM or resin, the answer depends on what you want to print. For small and detailed 3d prints, resin printers often come out ahead because they cure entire layers at once and reach fine detail levels. If you need large, simple 3d prints, you may find that FDM printers can be just as quick, but their print speed drops as the object gets bigger or more complex. You will see that which is faster FDM or resin changes based on size, detail, and how many 3d objects you print at once.
Key Takeaways
- Resin printers cure a whole layer at one time. This makes them faster for small prints with lots of detail. They are also fast when printing many things at once.
- FDM printers are good for big and simple models. They cost less money. But they get slower with tricky shapes or lots of objects.
- The height of each layer changes how long printing takes. Thicker layers print faster. But thick layers make prints less smooth and less detailed.
- Finishing the print takes extra time, especially with resin prints. Remember to plan for these extra steps.
- Pick resin if you want fine details or many small prints. Pick FDM if you want big prints or want to save money.
Technology Basics
FDM Overview
FDM is a popular 3d printing method. It uses a hot nozzle to melt plastic filament. The printer adds the melted plastic layer by layer. This builds your 3d object from the bottom up. Many people like FDM printers because they are simple and cheap. They are also easy for beginners to use. You can pick from many types of filaments. Some filaments have fibers like wood or carbon. These make your print stronger or more heat resistant. How you mix and prepare filaments changes the print’s strength and look.
FDM printers let you change settings like layer thickness and speed. These settings affect how fast your print finishes. They also change how smooth the print looks. Thin layers give better detail but take longer to print. FDM can make strong parts, but you might see lines between layers. Printing complex shapes or tiny details can slow things down. Sometimes, this causes small flaws on the surface.
Here is a table that compares FDM and resin printers for accuracy and feature size:
|
Technology |
Dimensional Tolerance (Typical) |
Minimum Feature Size |
Key Influencing Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
|
FDM (Desktop) |
±0.5% (±0.5 mm over 100 mm) |
~0.2 mm |
Extrusion spot size, gantry positioning, material shrinkage, layer thickness, nozzle diameter, print speed |
|
FDM (Industrial) |
±0.15% (±0.2 mm) |
~0.2 mm |
Same as desktop but with tighter control and calibration |
|
SLA (Resin-based) |
±0.15% to ±0.2% (±0.01 mm for 100 mm) |
~0.1 mm |
Resin properties, UV curing, layer thickness (~0.1 mm), post-processing shrinkage |
|
Carbon DLS (Resin) |
±0.1% (±0.1 mm for 100 mm) |
~0.1 mm |
Digital light projection, oxygen-permeable optics, resin chemistry, UV curing |
FDM printers are accurate, but resin printers can make even finer details.
Resin Overview
Resin 3d printing uses liquid resin and light. You pour resin into a tank. The printer uses UV light to cure each layer. There are different types of resin printers. SLA uses a laser. DLP uses a projector. LCD uses a screen to block UV light. All these types cure whole layers at once. This makes resin printing fast for small, detailed prints.
Resin printers can make smoother and more detailed prints than FDM. This is why people use them for miniatures, jewelry, and dental models. Resin printers usually have smaller build areas. The type of resin and the light’s power change print speed and quality. Some resins cure faster. Stronger lights can also speed up printing.
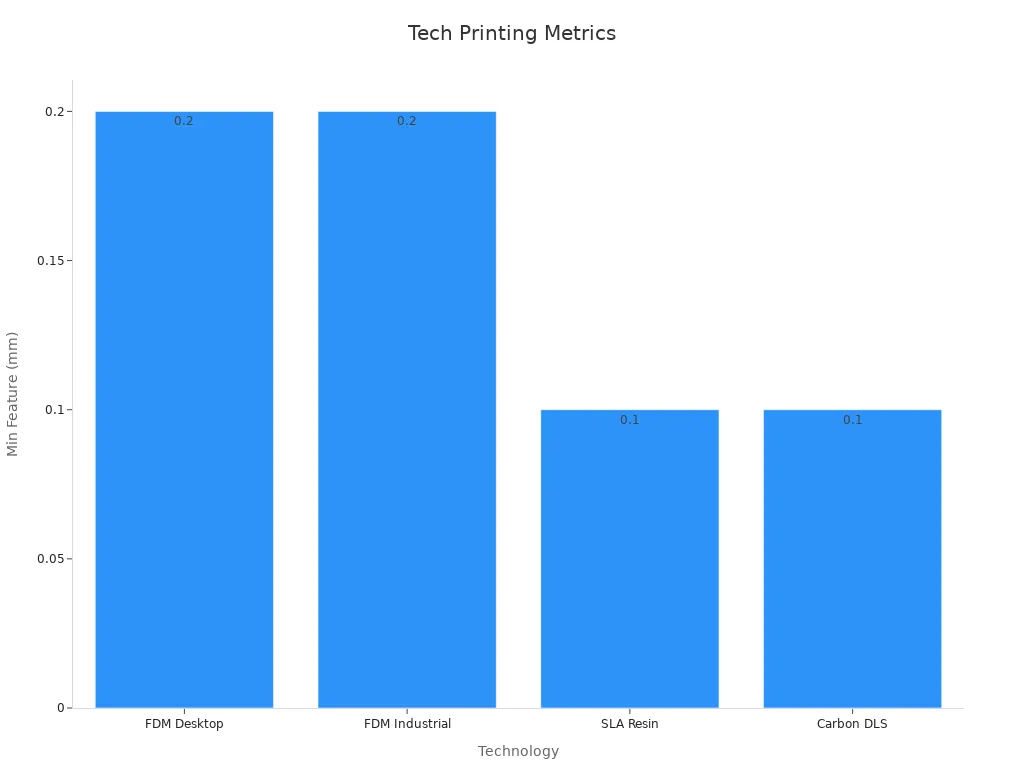
The chart shows resin printers can make much finer details. Resin printing is great for tiny features. You may need extra steps to finish your print.
Print Speed Factors

Layer Height
Layer height is one of the most important factors that affects print speed in 3d printing. When you use a smaller layer height, your 3d printers must lay down more layers to finish the model. This increases the total print time but gives you better detail and smoother surfaces. If you choose a thicker layer, your 3d printers finish faster, but you may lose some detail. For FDM printers, printing at 0.1 mm layer height takes about three times longer than printing at 0.3 mm. Resin printers also use layer height, but their print speed depends more on how fast each layer cures. You can get fine detail with resin, but the curing time per layer sets the pace.
Tip: If you want to print a large 3d model quickly, try using a thicker layer height. For intricate details, use a thinner layer.
Infill and Volume
Infill density and print volume also change how long your 3d prints take. FDM printers let you pick how solid your model is inside. A higher infill means more plastic and longer print time. Lower infill speeds up printing but makes the model lighter. Resin printers do not use infill in the same way. Most resin prints are hollow or have simple supports inside. This means print speed for resin depends more on the height and less on the volume.
|
Parameter |
Effect on Print Speed and Quality |
Optimal Values |
|---|---|---|
|
Printing Speed |
Affects dimensional accuracy and errors |
|
|
Layer Height |
Changes surface quality and print time |
0.2 mm for accuracy |
|
Infill Density |
Impacts accuracy and warpage |
60% for FDM |
|
Number of Layers |
Less effect on speed |
4 top/bottom layers |
Movement and Curing
FDM printers move the nozzle in three directions to build your 3d model. The more complex the shape, the more time the printer needs. If you print many objects at once, FDM print speed drops because the nozzle must travel to each part. Resin printers cure an entire layer at once, no matter how many objects you print. This makes resin print time almost the same for one or many models, as long as they fit on the build plate. This is a big advantage for batch printing.
Post-Processing
After printing, you must finish your 3d prints. Post-processing can take a lot of time. For FDM, you may need to remove supports or sand rough spots. Resin prints need washing and extra curing. Industry reports show post-processing can add 17% to 100% more time to your project. Sometimes, it even takes longer than the printing itself. If you plan to print many models, remember to include post-processing in your total print time.
Which Is Faster: FDM or Resin?

Single Object Speed
When you want to know which is faster fdm or resin for a single 3d print, you need to look at how each printer works. FDM printers build your 3d model by moving a nozzle and laying down melted plastic one layer at a time. Resin printers, like LCD and DLP types, cure an entire layer of liquid resin at once using light. This means resin print speed can be much faster for small and detailed prints.
For example, if you print a 10 cm tall 3d object, an FDM printer usually takes about 3 to 8 hours. A resin printer can finish the same model in 2 to 5 hours. LCD and DLP resin printers are the fastest because they cure whole layers at once. SLA resin printers use a laser to draw each layer, so they are a bit slower than LCD and DLP. You can see that resin 3d printing often wins when you want high detail and quick results for small models.
|
Aspect |
FDM Printer |
Resin Printer (LCD/DLP/SLA) |
|---|---|---|
|
Print time for 10 cm tall object |
3–8 hours |
2–5 hours |
|
Detail |
Good |
Excellent |
|
Print quality |
Visible layers |
Smooth, fine detail |
Note: FDM printers can go faster if you use a bigger nozzle or higher print speed, but this usually lowers the print quality. Resin printers keep high detail even at higher speeds.
Batch Printing Speed
Batch printing means you print many 3d models at once. Here, the difference between FDM and resin printers becomes clear. FDM printers must move the nozzle to each object, so the print time per model goes up as you add more models. If you print two objects, the time almost doubles. If you print ten, it can take ten times longer.
Resin printers work differently. They cure an entire layer across the whole build plate at once. If you fit ten models on the plate, the print time stays almost the same as printing one. This makes resin 3d printing much more efficient for batch jobs. You save a lot of time when you need many small, detailed prints.
|
Batch Printing Aspect |
FDM Printer |
Resin Printer |
|---|---|---|
|
Print time for multiple objects |
Increases with each object |
Stays about the same if objects fit |
|
Efficiency |
Lower for batches |
Very high for batches |
|
Best use |
Large, single prints |
Many small, detailed prints |
Tip: If you want to print a lot of miniatures or parts at once, resin printers give you the best efficiency and save you the most time.
Speed vs. Quality
You often face a trade-off between speed and quality in 3d printing. FDM 3d printing lets you change settings like layer height and print speed. If you use thicker layers and print faster, you finish sooner, but the surface gets rougher and you lose detail. High-speed fdm printing can help with big, simple prints, but you may see more lines and less accuracy.
Resin printers keep high detail even at faster speeds. You get smooth surfaces and fine features, even when you print many models at once. However, resin prints need more post-processing. You must wash and cure them after printing, which adds 20 to 40 minutes to your total time. FDM prints need less post-processing, so you can use them sooner.
Studies show that you can adjust FDM printer settings to balance speed and quality. For example, you can use a thicker layer for faster prints, but this lowers the mechanical strength and detail. Some new techniques, like local laser heating, help improve the bond between layers, so you get better quality without losing too much speed.
Remember: The fastest fdm printers can finish large, simple 3d prints quickly, but resin printers win for small, detailed, or batch prints. Always think about the trade-off between print speed and print quality before you start your project.
FDM vs. Resin: Choosing for Your Needs
Best for Large Prints
If you want to create large 3d models, fdm printers give you the best results. These printers offer big build volumes, sometimes up to 500×500×500 mm. You can print large objects in one piece, which saves time and reduces assembly steps. Fdm printing works well for prototypes, cosplay props, and engineering parts. You also get a wide choice of materials, including strong filaments for tough jobs. Performance reviews show that fdm printers can reach speeds up to 700 mm/s and cut production time by half compared to older methods. The chart below shows how fdm printers perform in large-scale printing:
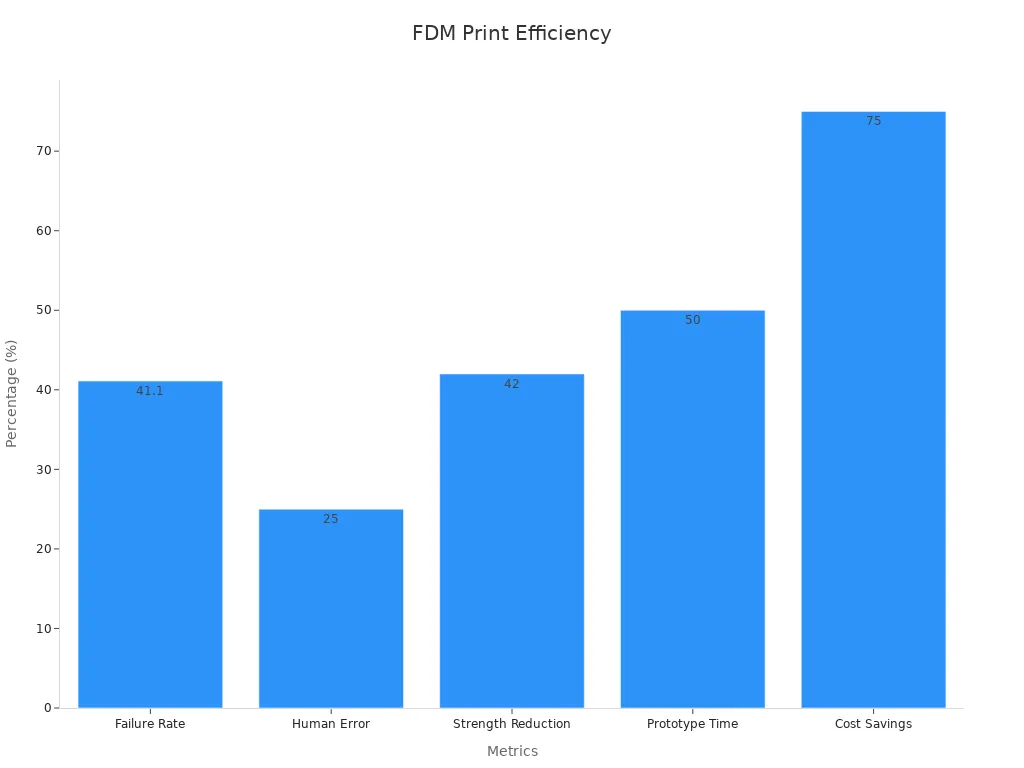
You may see some issues like warping or layer shifts, but you can fix these with good printer settings and careful monitoring.
Best for Detail and Miniatures
When you need intricate details or want to print miniatures, resin 3d printers stand out. These printers use light to cure each layer, which gives you smooth surfaces and sharp features. Resin printing can reach channel dimensions as small as 100 microns, making it perfect for jewelry, dental models, and tiny figurines. You can print several small models at once without losing speed or print detail. The table below compares fdm and resin printers for fine work:
|
Technology |
Typical Channel Dimension (µm) |
Best Printing Time (hours) |
|---|---|---|
|
SLA Resin |
<0.5 |
|
|
FDM |
~40 (reported best) |
Faster than SLA |
You get the highest quality and detail with resin, especially for small, complex 3d prints.
Cost and Workflow
You should think about both cost and workflow before choosing your 3d printer. Fdm printers cost less to buy and use cheaper filaments. You can start with a basic fdm printer for $200–$300, and filament costs $20–$50 per kilogram. Resin printers cost more, with entry models starting at $1000 and resin at $50–$200 per liter. Resin printing is faster for small, detailed models, but you spend more on materials and maintenance. Fdm printing takes longer for small parts but is more cost-effective for large, simple prints. The table below shows a quick comparison:
|
Aspect |
FDM Printers |
Resin (SLA) Printers |
|---|---|---|
|
Initial Equipment |
$200–$300 |
$1000–$3000 |
|
Material Costs |
$20–$50/kg |
$50–$200/liter |
|
Print Speeds |
4–12 hours |
1–4 hours |
|
Operational Costs |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Best Use |
Large/simple prints |
Small/detailed prints |
Tip: If you want to print many small, high-detail 3d models, resin printers save you time. For big, simple projects, FDM printers keep your costs low and let you print at larger scales.
Pick your 3d printer based on what you want to make. Resin printers are good for small prints with lots of detail. They are faster and show more detail than FDM printers. FDM printers are better for big models and cost less in the long run. How fast your print finishes depends on layer thickness, model shape, and how you place it on the printer. Always think about both printing and finishing steps when you plan your project. This helps you get the right mix of speed, quality, and efficiency.
-
Reviews show that printing flat saves time for small groups of prints. Printing tall works better for bigger models.
FAQ
How does print speed change if you print more than one object at a time?
Resin printers cure all objects in one layer at once. Print time stays almost the same. FDM printers print each object one by one. Print time increases with every extra object.
Can you make FDM prints faster without losing too much quality?
You can use a thicker layer height or a larger nozzle. This speeds up printing. You may see rougher surfaces, but for simple shapes, the quality stays good. Try different settings to find the best balance.
Do resin prints always need more post-processing than FDM prints?
Yes, resin prints need washing and extra curing after printing. FDM prints often need only support removal or light sanding. Resin post-processing takes more time but gives smoother results.
Which printer type is better for beginners who want fast results?
FDM printers are easier to set up and use. You can start printing quickly. Resin printers need more steps and safety gear. For fast, simple prints, FDM works best for beginners.
Does print orientation affect speed for both printer types?
Yes, print orientation changes print time. Printing objects flat on the build plate usually finishes faster. Printing tall objects takes longer because the printer adds more layers.

















Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.