Getting good results from your 3D printer starts with picking the right filament. Have you noticed why some prints look smooth but others fail badly? Most of the time, it’s not your printer—it’s the filament. A good-quality 3D printing filament makes strong, accurate, and steady prints. A bad one can cause clogs, weak layers, and wasted time.
When performing a 3D printing filament quality check, ask: Is the material the same size all through? Is it stored well to keep out moisture? Is it from a trusted brand? A quick 3D printing filament quality check can save trouble and help find the best filament for both beginners and experts.
🛠️ Tip: Always check the box and certifications before buying a filament. This small step can improve your printing results a lot.
Key Takeaways
- Pick filaments with even thickness and precise size. This helps prints stay smooth and avoids clogs.
- Use filaments made from pure materials. Clean filaments make stronger prints and cause fewer problems.
- Look for packaging that keeps out moisture. Good brands seal filaments in vacuum bags with drying packs.
- Read about brands and check reviews. Reliable brands have certifications and good comments from users.
- Try small filament samples before buying a lot. This lets you check quality and if it works with your printer.
Key Factors in a 3D Printing Filament Quality Check
Choosing the right filament is crucial for successful 3D printing. Let’s explore three important things to look for in a good filament to avoid problems.
Consistency in Diameter and Tolerance
Have your prints ever failed because of clogs or weak layers? This often happens when the filament has uneven thickness. A good filament stays the same size all the way through, helping your printer work smoothly and accurately.
Manufacturers use special tools to check filament size. For instance, 3-axis systems can spot tiny changes like 0.13 mm in 1.75 mm filaments. In comparison, 2-axis systems allow up to 0.36 mm of variation. Even small differences can affect your print quality a lot.
Here’s a simple comparison of diameter consistency:
|
Measurement Type |
Percentage of Diameter |
Measurement at 1.75 mm |
Measurement at 2.85 mm |
|---|---|---|---|
|
3-axis |
7% |
0.13 mm |
0.22 mm |
|
2-axis |
20% |
0.36 mm |
0.59 mm |
For the best prints, pick filaments with a tolerance of ±0.03 mm or tighter. Some brands, like Prusament, offer tolerances as low as ±0.02 mm. Avoid filaments with tolerances over ±0.10 mm, as they are often poorly made or recycled.
🛠️ Tip: Look for diameter tolerance details on the spool or box. If it’s missing, that’s a warning sign.
Material Composition and Purity
Not all filaments are the same. The type of material affects how well it performs. For example, PLA is easy to use, while ABS is stronger and resists heat better. But even within these types, the material’s purity is very important.
High-quality filaments are made from clean, new materials. They don’t have recycled plastics or dirt that can mess up your prints. Impurities can cause clogs, uneven layers, and weak prints.
Here are some checks good manufacturers use:
|
Quality Control Measure |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Finds impurities to keep print quality high. |
|
|
Tensile Strength Testing |
Tests how much the filament can stretch without breaking. |
|
Layer Adhesion Assessment |
Checks how well layers stick together during printing. |
Think about what your project needs when picking a filament. For example, ABS is better than PLA for strong, functional parts.
🛠️ Tip: Choose trusted brands that share clear material details. This helps you get the right filament for your project.
Packaging and Moisture Protection
Did you know water can ruin your filament? Materials like PLA and ABS soak up moisture from the air. This can cause bubbles, stringy prints, and weak layers.
Good packaging protects your filament from moisture. High-quality brands vacuum-seal their spools and include desiccant packs. Some even provide resealable bags for storage.
Here’s what proper packaging looks like:
|
Quality Control Measure |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Moisture Content Monitoring |
Keeps track of moisture levels for better printing. |
|
Packaging and Storage Control |
Uses sealed packaging to block moisture and dirt. |
If a spool is loosely packed or missing a desiccant, it’s better to skip it.
🛠️ Tip: Store your filaments in airtight containers with silica gel to keep them fresh longer.
By focusing on diameter consistency, material purity, and packaging, you’ll get better prints and fewer problems.
Printer Compatibility and Application Suitability
Not every filament works with all 3D printers. Picking the right filament for your printer and project is very important. Problems like warping, clogs, or bad adhesion may happen if the filament doesn’t match your printer.
Some filaments need special printer features to work well. For example, certain materials need high heat or enclosed spaces to avoid warping. Flexible filaments need a direct-drive extruder for smooth feeding. Knowing your printer’s limits can save time and effort.
Here’s a simple guide to match filaments with printers and uses:
|
Filament Type |
Recommended Printer Type |
Nozzle Size |
Printing Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ABS, ASA, PC, PA |
Enclosed Printers (e.g., Bambu X1, X1C) |
0.4 mm or 0.6 mm |
Higher heatbed and chamber temperatures |
|
PLA, PETG, TPU |
Open-frame or Enclosed Printers |
0.4 mm |
Standard conditions, less prone to warping |
|
Carbon Fiber/Glass Fiber Reinforced |
Enclosed Printers recommended |
0.6 mm preferred |
Higher temperatures, avoid clogging risks |
Always check your printer’s specs when picking a filament. Does it support the right nozzle size and temperature? For tough materials like carbon fiber filaments, use a hardened steel nozzle to avoid damage.
🛠️ Tip: If you’re unsure, start with PLA. It’s easy to use and works with most printers.
Choosing the right filament for your project is also key. For strong, heat-resistant parts, ABS or nylon is better. For decorative items, PLA is easier and gives a smooth finish. By knowing your printer’s abilities and your project’s needs, you’ll get great results with less trouble.
Common Signs of Low-Quality 3D Printing Filament
Finding bad filament early can stop printing problems. Watch for these signs to check filament quality.
Brittle and Breakable Filaments
Has your filament ever snapped while loading it? This shows it’s brittle. Cheap filaments, like PLA, break easily due to poor materials or bad storage. Brittle filaments can cause uneven feeding, leading to weak or gapped prints.
To test, bend a small piece of filament. Good PLA bends a little before breaking. If it snaps right away, it’s likely bad. ABS is stronger but shouldn’t feel too fragile. Fragile filaments waste time and materials, so avoid them.
🛠️ Tip: Keep filaments in a cool, dry place to stop brittleness from moisture.
Uneven Thickness or Flaws
Uneven filament thickness can ruin prints. If the size changes while printing, it may clog or cause uneven extrusion. These problems waste time and mess up prints. Cheap filaments often have bumps, scratches, or uneven colors.
To check, roll the filament between your fingers and look closely. Use a caliper to measure thickness at different spots. Good filaments, like PLA or ABS, stay the same size all through. If you see flaws, skip that filament.
🛠️ Tip: Pick filaments with a tolerance of ±0.03 mm or less. This helps smooth feeding and better prints.
Bad Packaging and Storage
Packaging shows how good a filament is. Good brands vacuum-seal spools and add desiccant packs to block moisture. Poorly stored filaments soak up water, causing bubbles, stringing, and weak prints. PLA and ABS are especially sensitive to water.
If the spool looks dusty, loosely packed, or not sealed well, it’s a bad sign. Even if it looks okay, bad storage can ruin its quality. Always pick filaments with good packaging and store them in airtight containers.
🛠️ Tip: Use resealable bags or storage boxes with silica gel to keep filaments fresh.
By checking for brittleness, uneven thickness, and bad packaging, you’ll avoid low-quality filaments. Your prints will turn out much better!
Missing Certifications or Quality Checks
Have you noticed why some filaments work better than others? The answer often lies in certifications and quality checks. If a filament doesn’t have these, it’s a warning sign. You might deal with bad prints, clogs, or wasted material.
Certified filaments are tested to meet strict industry rules. These tests check the filament’s size, material, and performance. Without certifications, you can’t trust the filament’s quality. It’s like buying a bike without knowing if it’s safe to ride.
Here’s what to check for certifications:
- ISO Standards: Proves the filament meets global quality rules.
- RoHS Compliance: Confirms the filament is free of harmful chemicals.
- Brand Guarantees: Some brands, like Prusament, offer their own quality promises.
🛠️ Tip: If the box doesn’t show certifications, avoid that filament. Good brands proudly list their standards.
No certifications might also mean the filament has recycled or dirty materials. These can make it brittle, uneven, or cause weak layers. You’ll spend more time fixing problems than printing.
Here’s a simple comparison of certified vs uncertified filaments:
|
Feature |
Certified Filaments |
Uncertified Filaments |
|---|---|---|
|
Diameter Consistency |
±0.03 mm or tighter |
Often exceeds ±0.10 mm |
|
Material Purity |
High-quality virgin resin |
May contain impurities |
|
Performance Reliability |
Consistent and predictable |
Varies widely |
Picking certified filaments saves time and gives better prints. Next time you shop, look for certifications. They help you get smoother prints with fewer problems.
How to Pick 3D Printer Filaments for Your Projects
Choosing the right filament can seem confusing with so many choices. Don’t worry—this guide will help you find the best filament for your project. You’ll learn how to match filament types, balance cost and quality, and check brand reputation.
Picking Filament Types for Your Project
Different projects need different filaments. Knowing how materials work helps you choose the right one. For example, PLA is easy to use and great for decorations. It prints smoothly and works well for beginners. ABS, however, is stronger and handles heat better, making it ideal for tough parts.
Here are examples of filaments for specific uses:
- PLA: Best for prototypes, decorations, and light-use parts. It’s simple to print and fits most printers.
- ABS: Great for strong parts like cases or mechanical pieces. It resists heat but needs an enclosed printer to avoid warping.
- Wood-PLA Blends: Perfect for artistic designs. These filaments look like wood but aren’t as hard as real wood.
🛠️ Tip: Unsure where to start? Try PLA. It’s flexible and works for most projects.
Balancing Price and Quality
Cheap filaments might seem like a good deal, but they often cause problems. They can clog your printer, make weak layers, or ruin prints. High-quality filaments cost more upfront but save money by reducing failed prints and extra work.
Here’s a comparison of high-quality vs low-quality filaments:
|
Factor |
High-Quality Filaments (Polylite) |
Low-Quality Filaments |
|---|---|---|
|
Saves Money Over Time |
Yes |
No |
|
Less Post-Processing Needed |
Yes |
No |
|
Printed Part Strength |
High |
Low |
|
Variety of Options |
Many |
Few |
|
Time Efficiency |
High |
Low |
For example, Polylite PLA gives reliable results and strong prints. Cheap filaments may seem cheaper but often lead to wasted time and materials.
🛠️ Tip: Think about the total project cost, including failed prints. Quality filaments save time and money.
Checking Brand Reputation and Reviews
Not all filament brands are trustworthy. Some focus on quality, while others cut corners. Researching brands and reading reviews can help you avoid bad products. Reliable brands like Prusament or Polymaker share details about their filaments, like size accuracy and material purity.
When choosing a brand, look for:
-
Certifications: Brands with ISO or RoHS standards offer better quality.
-
Reviews: Read online feedback to see how others rate the filament.
-
Transparency: Good brands explain their manufacturing process and quality checks.
For example, Prusament has a size tolerance of ±0.02 mm, which ensures smooth printing. Uncertified filaments often lack precision, causing uneven prints and clogs.
🛠️ Tip: Join 3D printing groups to get advice and learn from others. They can help you find trusted brands.
By choosing the right filament type, balancing price and quality, and researching brands, you’ll get better prints and fewer problems.
Testing Filament Samples Before Bulk Purchases
Buying a lot of filament can save money, but it’s risky if the quality is bad. Testing a small sample first is a smart idea. It helps you see how the filament works with your printer and project.
Why Test Filament Samples?
Samples let you check important things like print quality and strength. A quick test can show problems like brittleness or poor layer sticking. It’s better to find these issues early than waste time on bad prints.
Here’s what you can learn from testing:
-
Print Quality: Look for smooth layers and even extrusion.
-
Strength and Durability: See if the printed part is strong.
-
Printer Compatibility: Make sure the filament works with your printer.
🛠️ Tip: Many brands sell small sample packs. These are great for testing without spending too much.
How to Test Filament Samples
Testing is easy if you follow these steps:
- Check the Filament: Look for bumps, uneven thickness, or discoloration. Use a caliper to measure the size at different spots.
- Print a Test Object: Try printing a simple model like a cube or boat. This shows problems like warping or bad layer sticking.
- Test Strength: Gently press the printed part. Does it bend or break? Good filaments should not snap easily.
- Adjust Settings: Change temperature or speed to get better results. Some filaments need small tweaks to print well.
🛠️ Tip: Write down how each filament performs. This helps you compare brands later.
What the Data Says About Filament Testing
Testing isn’t just guessing—it’s based on facts. Studies show how different materials handle stress. For example:
- PLA printed flat and on its side had similar stiffness.
- Adding more perimeters made flat prints stronger.
- Comparing stiffness helps predict how a filament will work in real life.
These facts show why testing is important. A quick test print can tell you how a filament behaves, so you can choose wisely.
When to Skip Bulk Purchases
If the sample fails, don’t buy more. Watch for these warning signs:
- Inconsistent Diameter: Can cause clogs or uneven printing.
- Poor Layer Adhesion: Makes prints weak and fragile.
- Stringing or Warping: Shows bad material quality.
🛠️ Tip: If one brand fails, try another. There are many options to explore.
Testing samples saves money and avoids problems. It’s a small step that leads to better prints and less frustration.
Practical 3D Printing Filament Quality Check Methods
Look Closely for Flaws
Before using the filament, examine it carefully. A quick look can show its quality. Check for bumps, scratches, or uneven colors. These problems can cause clogs or messy printing. Roll the filament between your fingers to feel for uneven thickness. If it feels rough or bumpy, it’s not a good choice.
Also, check how the filament is wound on the spool. A neatly wound spool feeds smoothly into the printer. A tangled spool can cause jams. For materials like PLA, a smooth surface is important for good prints.
🛠️ Tip: Use a caliper to measure the filament thickness at different spots. Even thickness helps smooth printing.
Print Small Tests to Check Quality
Printing small test models is a great way to check filament quality. Start with something simple, like a cube or small figure. This helps you see how the filament works and how the print looks. Watch for problems like stringing, warping, or weak layers.
- Measure the filament thickness and set it in your slicer.
- Adjust the temperature and extrusion settings for the filament.
- Print the model and watch for any issues during printing.
- Check the printed object for smooth layers and strong bonding.
- Make changes if needed and reprint to compare results.
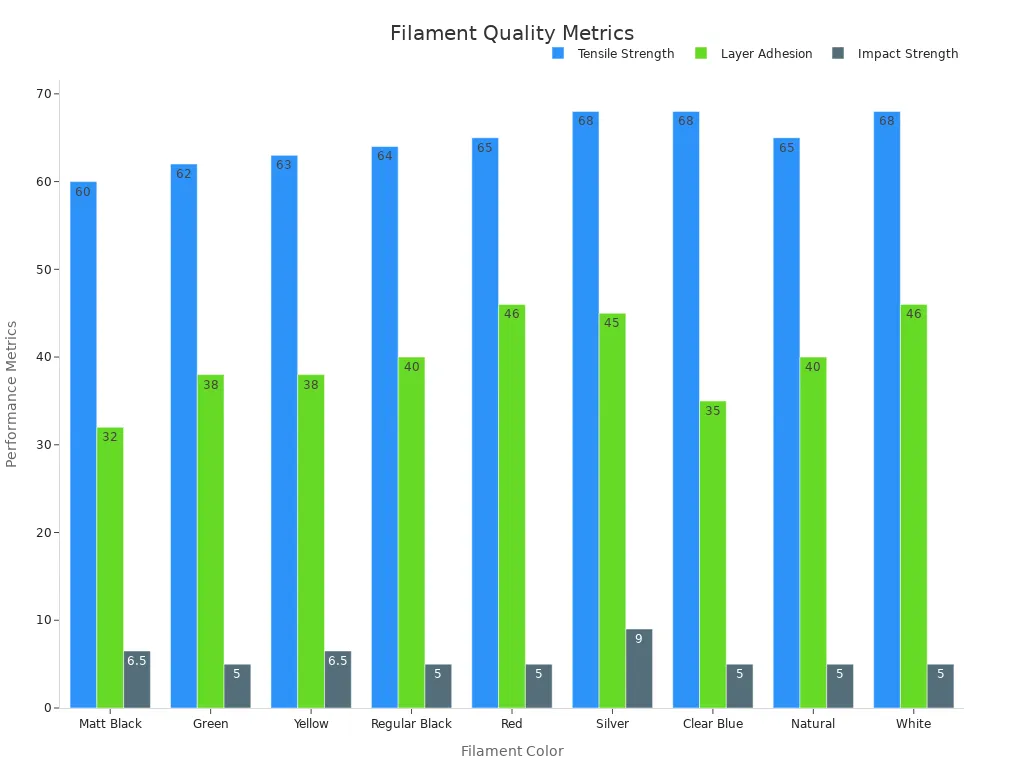
Here’s a table showing how different filament colors perform:
|
Filament Color |
Tensile Strength (MPa) |
Layer Adhesion (MPa) |
Impact Strength (kJ/m²) |
Warping (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Matt Black |
60 |
32 |
6.5 |
10+ |
|
Green |
62 |
38 |
5 |
10+ |
|
Yellow |
63 |
38 |
6.5 |
10+ |
|
Red |
65 |
46 |
5 |
10+ |
|
White |
68 |
46 |
5 |
4-7 |
🛠️ Tip: For PLA, start with a nozzle temperature of 200°C. Adjust if needed.
Look for Certifications from Manufacturers
Certifications help ensure the filament is high quality. Good manufacturers test their products to meet strict rules. Look for certifications like:
- ISO 9001: Proves the filament meets quality standards.
- RoHS Compliance: Confirms the filament is safe and free of harmful chemicals.
- UL 746: Tests the material’s strength and heat resistance.
Some certifications, like UL 746A, check short-term performance. Others, like UL 746B, test long-term durability. These certifications show the filament can handle different conditions.
By inspecting, testing, and checking certifications, you can find filaments that give great results every time.
Reading User Reviews and Community Feedback
When buying 3D printing filaments, user reviews can help a lot. They show real experiences that brands might not mention. Instead of just reading product details, learn from others to choose better.
Check reviews on sites like Amazon, Reddit, or 3D printing forums. Look for patterns in what people say. Do they praise the filament for being smooth and reliable? Or do they complain about clogs, breaking, or bad packaging? Read both good and bad reviews for a full picture.
🛠️ Tip: Find reviews from people using similar printers or projects. Their advice will match your needs better.
Community forums and social media groups are also helpful. People share reviews, tips, and photos of their prints. You can ask questions and get advice for your printer. For example, if you’re unsure about a filament, someone may have already tested it.
Here’s how to use user feedback wisely:
- Spot patterns: One bad review isn’t a big deal, but many are a warning.
- Check recent reviews: Brands sometimes improve products, so newer reviews matter more.
- Join discussions: Ask questions in groups. Most users are happy to help.
💡 Note: Be careful with reviews that seem too perfect. Real reviews often include specific details about the filament.
By using reviews and community advice, you can avoid bad filaments. This helps you pick ones that work well and save time. It’s like having experts guide you!
Finding good 3D printing filaments helps save time and money. Check for even thickness, good packaging, and reliable certifications. Quality filaments make smoother prints and stronger parts. They also reduce printing problems. Always pick filaments that fit your printer and project. Choosing the right materials gives better results and makes 3D printing more enjoyable.
FAQ
What’s the best filament for beginners?
PLA is great for beginners. It’s simple to use and works with most printers. You don’t need special settings, and it’s budget-friendly. PLA also gives smooth prints, making it perfect for learning.
🛠️ Tip: Buy a small spool first to test it out.
How do I store 3D printing filaments properly?
Keep filaments in airtight containers with silica gel to stay dry. Moisture can damage them, causing weak prints or stringing. Vacuum-sealed bags are also helpful. Store spools in a cool, dry place away from sunlight.
💡 Note: Look for resealable packaging when buying filaments.
How can I tell if a filament is too old to use?
Old filaments may snap easily or absorb moisture. If prints have bubbles or stringing, it’s likely too old. Bend a small piece or print a simple model to check its condition.
🛠️ Tip: Use a filament dryer to fix slightly damp spools.
Are expensive filaments always better?
Not always. Some cheaper brands work well, while pricey ones might not. Focus on certifications, reviews, and material details instead of cost. Testing a sample is the best way to know quality.
💡 Tip: Choose brands with clear diameter tolerances and pure materials.
Can I use any filament with my 3D printer?
Not all filaments fit every printer. Check your printer’s specs for nozzle size, temperature, and compatibility. Flexible filaments need direct-drive extruders, and ABS needs enclosed printers to avoid warping.
🛠️ Tip: If unsure, start with PLA—it works with most printers.




















Deixe um comentário
Todos os comentários são moderados antes de serem publicados.
Este site está protegido pela Política de privacidade da hCaptcha e da hCaptcha e aplicam-se os Termos de serviço das mesmas.