To pick the best big 3D printer, follow these 10 tips:
- Know what your project needs
- Check how big it can print
- Look at how good the prints are
- Make sure it uses the right materials
- See if it works well every time
- Think about how fast it prints
- Find out if it has cool features
- Check if it keeps prints safe and steady
- Try the software and see if it connects easily
- Look at the price and what others say
A 500*500*500mm 3D printer is good for big things. It works for large models, furniture, or test samples. Big print space and strong frames help with tough jobs.
Pick a printer that fits your project, job, and future needs.
Key Takeaways
- Pick a 3D printer that matches your project size.
- Make sure it can use the materials you need.
- This helps you get strong and accurate prints.
- Find printers with a big build area, like 500x500x500mm.
- Big build areas let you print large things in one piece.
- This saves you time because you print all at once.
- Choose printers with auto-bed leveling and filament sensors.
- A strong frame helps stop printing mistakes.
- Good software and easy connections make printing simple.
- You can control and watch your prints live.
- This helps you work faster and easier.
- Think about the total price and how well it works.
- Check what other users say about the printer.
- Pick a printer that is reliable and saves money over time.
Define Project Needs
Application and Industry
Think about how you will use your large format 3D printer. Different jobs need different things. Architects need detailed, accurate models. Car and plane makers want strong parts from special stuff. Doctors need clean, exact prints for tools or samples.
Tip: Pick a printer with features that match your job. This saves money and time.
Here are some things to think about:
- Material type: Some jobs need bendy or heat-safe stuff.
- Accuracy: Parts that fit together need to be exact.
- Print size: Big things need a big print area.
- Work space: Some materials need heat or covers.
The right printer for your 3d print applications gives better results. Using PLA instead of ABS can stop warping and make prints look nicer. Filament sensors and power loss help finish long prints.
Check these industry numbers to help you choose:
|
Metric Category |
Focus |
Why It Matters for 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
|
Strong mesh, thick walls |
Stops weak spots and failed prints |
|
|
Geometric Accuracy |
Correct size |
Makes sure parts fit and work |
|
Completeness Metrics |
Full shape, good coverage |
Needed for tricky or detailed models |
|
Visual Quality |
Nice texture and surface |
Good for show models and samples |
Project Scale
Measure your project’s size and detail before you pick. Big projects need printers with lots of space and good detail. To print furniture or big samples, you may need a bed size of 900 mm × 1100 mm × 770 mm or more.
Being exact is important. Repeatability means the printer makes the same part every time. Dimensional accuracy shows how close the print is to your plan. Nozzle size and motor steps change how much detail you get. For tiny details, use a small nozzle and fine motors.
Other things to check:
- Layer height: Thin layers make smoother prints.
- Material: Some plastics shrink or bend more.
- Heat control: Heated beds and covers stop warping in big prints.
- Strong frame: A tough frame keeps prints right, even when big.
Knowing your project’s size helps you pick the right printer. This stops problems with big prints.
Build Volume
Picking the right build volume is very important. Build volume means how big your prints can be. If you want to make furniture or car parts, you need a large build volume. Most regular printers only print up to 200x200x200mm. This size is too small for big things. A large format 3d printer starts much bigger. It lets you print larger objects.
500*500*500mm 3D Printer
A 500500500mm 3d printer is great for big jobs. You can print large items in one piece. This saves time and makes parts stronger. You do not have to glue or bolt pieces together. Many people in architecture, cars, and healthcare use this size. It fits most big models and samples. If you want to print furniture or machine parts, this printer gives you space. Some printers are even bigger, up to 1.5 x 1.5 x 2 meters. These can make even larger things and work faster.
Tip: Make sure your large format 3d printer has a strong frame. Look for auto-bed leveling and filament sensors. These help you finish long prints without trouble.
|
Printer Type |
Typical Build Volume |
Best For |
|---|---|---|
|
Standard 3D Printer |
200x200x200mm |
Small models, toys |
|
500*500*500mm 3d printer |
500x500x500mm |
Furniture, prototypes, tools |
|
Extra Large-Format Printer |
1500x1500x2000mm |
Industrial, automotive, molds |
Future Expansion
Think about what you might need later. The printing world keeps changing. New jobs may need even bigger build volumes. Many companies want printers that can grow with their needs. As 3D printing grows in cars and healthcare, you may need a printer that can do more. New materials and on-demand jobs also need bigger build volumes.
Note: Planning ahead means you will not need to buy a new printer every time your projects get bigger.
A large build volume lets you print bigger things. It also lets you print more items at once. This saves time and money for small batches. When you pick a large format 3d printer, think about your current and future projects. This way, your printer will not hold you back.
Print Quality
Resolution
You want your large format 3D printer to create sharp, detailed prints. Resolution tells you how fine the details can be. For big projects, a high resolution keeps your models clear, even when you print them large. If you use a low resolution, your prints may look blurry or pixelated.
Here are the most important resolution benchmarks for high-quality large format prints:
- Keep your image resolution at 300 DPI or higher for sharpness.
- Think about how far people will view your print. Prints seen from far away can use lower DPI.
- Low DPI causes pixelation and loss of detail when you make prints bigger.
- Image interpolation can help a little, but it cannot match a true high-resolution file.
- Pixel density (PPI) and file format matter, but DPI is the main number to watch.
Tip: Always check your printer’s specs for maximum DPI and layer height. A smaller layer height gives you smoother surfaces and better detail.
Surface Finish
Surface finish affects how your printed parts look and feel. A smooth finish makes your models look professional and helps with painting or assembly. You can improve surface finish by adjusting print settings or using post-processing methods.
|
3D Printing Technology |
Average Roughness (Ra, µm) |
Maximum Roughness (Rz, µm) |
|---|---|---|
|
SLA (As printed) |
1.5 |
10.1 |
|
Carbon DLS (As printed) |
1.22 |
11.1 |
|
FDM (Perpendicular) |
22.5 |
114.9 |
|
FDM (Along layers) |
0.9 |
N/A |
|
SLS (As printed) |
10-12 |
59.9-69.4 |
|
SLS (After polishing) |
4.4 |
31.1 |
|
DMLS (Bead blasted) |
6-12 |
39.8-69.4 |
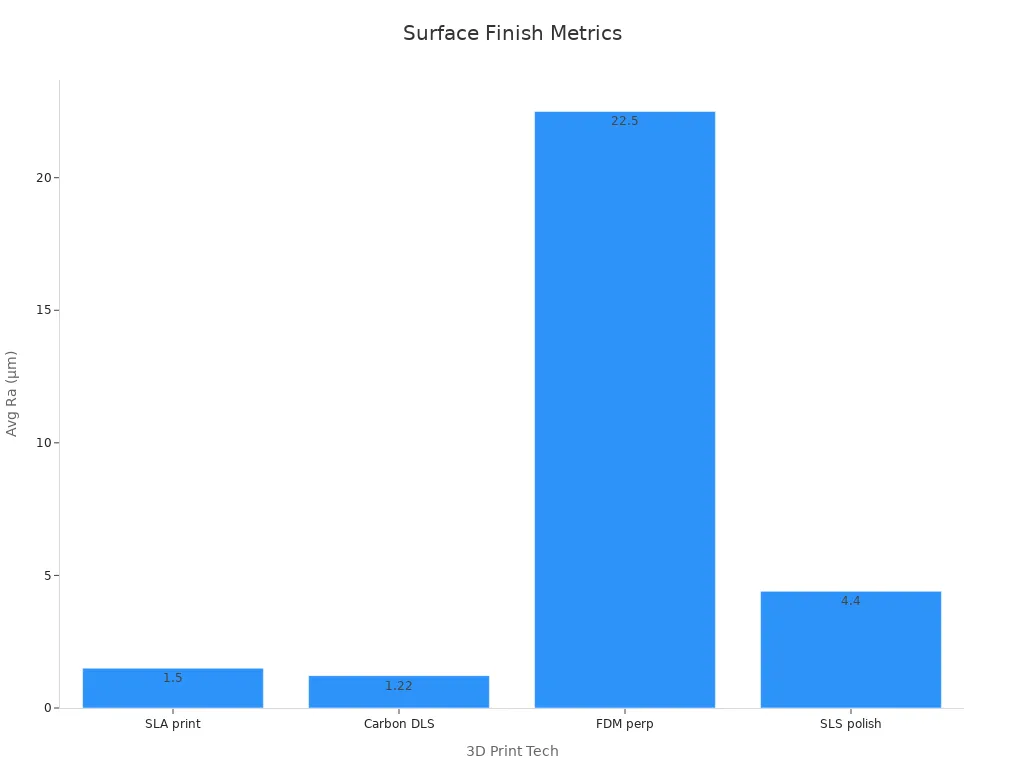
You can use methods like electro-polishing, shot blasting, or barrel finishing to make surfaces smoother. Lower print speeds and a 90° print orientation also help. Layer height and raster angle change how rough the surface feels. For the best results, check your prints by looking, touching, and measuring with special tools.
Note: A large format 3D printer with good resolution and surface finish will make your big projects stand out.
Material Compatibility
Picking the right 3D printing material is important. Your big printer must work with the filament you want. Some printers let you use many types of filament. Others only work with certain brands or types. Think about what your project needs before you choose.
Filament Types
There are many filaments for large prints. Each one has special features. Use this table to compare the most common ones:
|
Filament Type |
Key Performance Attributes |
|---|---|
|
PLA |
Breaks down, easy to use, cools fast, sticks well |
|
ABS |
Strong, heat-safe, cools slow, sticks okay |
|
PETG |
Tough, bends, resists chemicals, easy to print |
|
Nylon |
Very tough, takes hits, needs drying first |
|
Carbon Fibre |
Very stiff and strong, good for light, tough parts |
|
TPU |
Bends like rubber, good for stretchy things |
Different filaments change how prints cool and stick. PLA cools fast and sticks well, so prints are strong. ABS cools slow to stop warping, but can be hard to stick. Nylon needs drying for best results. Closed printers limit your choices but are easier for new users. Filament sensors help you not run out during long prints. For big jobs, look for printers with more than one sensor.
Heated Bed and Nozzle
The heated bed and nozzle decide which materials you can use. A heated bed keeps prints flat and stops warping. The right nozzle heat helps layers stick and makes parts strong. Check this table for more info:
|
Parameter |
Effect on Material Compatibility |
Example Materials |
Recommended Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Nozzle Temperature |
Changes how plastic flows and sticks |
PLA |
Higher heat makes parts stronger |
|
|
|
ABS |
Not much change with heat |
|
Heated Bed Temperature |
Stops shrinking and bending, keeps size right |
ABS |
About 130 °C |
|
|
|
PLA |
About 70 °C |
Tip: Make sure your printer can reach the right heat for your filament. Closed printers set this for you. Open printers let you pick the heat.
Filament sensors help you watch your material and stop failed prints. If you want to use many filaments, pick an open printer with good sensors. This helps you finish big projects without problems.
Reliability
A reliable big 3D printer is very important. It helps you finish big jobs on time. If your printer works well, you avoid mistakes and save money.
Maintenance
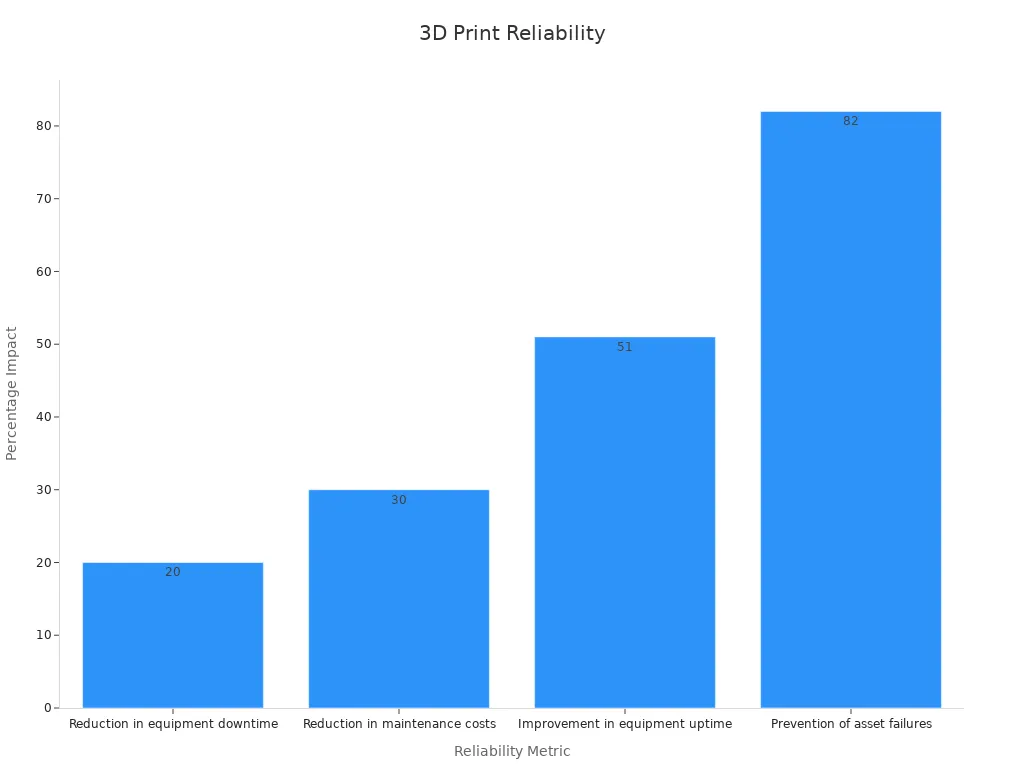
You must take care of your printer often. This keeps it working well. Fixing small problems early stops bigger issues later. Some printers remind you to check them every 500 hours. These reminders help you fix things before they break. Smart sensors can watch heat and pressure. If something is wrong, the printer tells you fast.
Here is how smart care helps:
|
What It Means |
How It Helps Big 3D Printing |
Example or Source |
|---|---|---|
|
Less time not working |
Reminders every 500 hours keep the printer running |
|
|
Lower repair costs |
Up to 30% less cost with real-time checks |
Sensors find problems early and ask for quick fixes |
|
More time working |
Up to 51% more uptime with data tracking |
Data shows what breaks often and helps plan repairs |
|
Stops most breakdowns |
Up to 82% of failures stopped by smart care |
Good reports and alerts help keep the printer healthy |
Smart care and fast checks make a big difference. Oil and alerts help you not forget important tasks.
Downtime
Downtime means your printer is not printing when you need it. Even short stops can waste time and materials. This can make customers upset. Watch numbers like uptime, MTBF, and MTTR. Try to keep uptime at 98% or more each month. If you see more stops, check your care plan or think about a new printer.
Try to get close to 100% uptime for big jobs. Good parts and cooling, like liquid cooling, stop problems. Fast health checks help you find issues early and keep printing.
To have less downtime, pick printers with alerts and strong parts. This helps you finish jobs and keeps customers happy.
Print Speed
Throughput
Print speed matters a lot when you work on big projects. You want your large format 3D printer to finish jobs quickly and keep up with your needs. When you look at speed, do not just check the number in millimeters per second (mm/s). That number shows how fast the print head moves, but it does not tell the whole story. You should also look at volumetric extrusion speed. This tells you how much material the printer can lay down each second. For most medium-quality prints, you will see speeds around 50–60 mm/s. Some printers claim up to 200 mm/s, but real-world speeds are often lower because of material limits and how fast the print head can move.
Tip: PLA prints faster than ABS or TPU. If you want speed, choose materials that melt and flow easily.
You can use this table to understand key speed and efficiency metrics:
|
Metric Name |
Description |
Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
|
Prints finished per day or week |
Shows how much you can produce |
|
|
Capacity Utilization |
Percent of printer’s output used |
Helps spot slowdowns or bottlenecks |
|
Lead Time |
Time from start to finish for a print job |
Shorter lead time means faster jobs |
|
Cycle Time |
Time to finish one print |
Affects how many jobs you can run |
High throughput means you can finish more prints in less time. For big projects, aim for printers with machine uptime above 95% and production turnaround times of 6–8 hours per cycle. This keeps your workflow smooth and your projects on track.
Batch Printing
Batch printing lets you print many parts at once. This is a smart way to save time and lower costs, especially for large projects. When you group jobs together, you reduce setup time and make better use of your printer. Many companies see up to 30% faster processing and fewer material shortages when they use batch printing.
Here are some real-world gains from batch printing:
|
Context/Industry |
Performance Gain |
Impact |
|---|---|---|
|
E-commerce |
30% faster order processing |
Quicker shipping and happy customers |
|
Publishing |
30% fewer material shortages |
Fewer delays and smoother production |
|
General Operations |
Lower setup and labor costs |
More prints, less downtime, higher savings |
Batch printing also helps you track print speed, error rates, and maintenance. This makes it easier to spot problems early and keep your printer running well.
If you want to print big batches, look for a large format 3D printer with a big build volume and smart software. This lets you fill the print bed with many parts and finish more work in less time. Batch printing is a key way to boost productivity for big projects.
Features and Modularity
Self-Leveling Bed
You want your big 3D printer to work well. Auto-bed leveling helps with this. The printer uses sensors to check the bed. It looks at many spots on the surface. The printer makes a map of the bed. Then, it moves the nozzle up or down as needed. This gives you even layers and strong sticking. Auto-bed leveling stops prints from failing because of uneven beds.
Many printers use a 25-point check for leveling. This means the printer checks 25 places on the bed. It can fix small bumps or dips by itself. You do not need to fix the bed by hand. Dual Z motors help move the print head up and down. This makes prints better and mistakes fewer.
Auto-bed leveling saves time and makes printing easier. You can start big projects without worry.
Auto-bed leveling works with smart software. Features like pressure advance help make smooth layers. You see fewer lines and nicer surfaces. Even on big beds, prints look sharp with auto-bed leveling.
Modular Large-Format 3D Printer
A modular 3D printer lets you change parts easily. You can upgrade or fix things fast. Many modular printers have strong frames and steel plates. These keep the printer steady during big jobs. You can swap the nozzle, bed, or other parts when needed.
Here is a table showing how modular features help:
|
Feature/Component |
Key Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Modular frame |
Easy to build, strong, good for big prints |
|
Bed plate |
Stays flat, works well with auto-bed leveling |
|
Nozzle head |
Makes prints neat and correct |
|
Modular design overall |
Works with many materials, easy to upgrade |
A strong, modular frame helps auto-bed leveling work best. You get better prints and less waiting. Modular printers let you try new materials like PLA, ABS, or TPU. You can keep your printer new as your needs grow.
Picking a printer with auto-bed leveling and modular design is smart. You get better prints, easy upgrades, and less fixing.
Auto-bed leveling and modular parts make your big 3D printer ready for any job. You save time, make fewer mistakes, and have more choices.
Enclosure and Environment
Temperature Control
Your large format 3D printer needs a steady place to work. Enclosures help keep the heat inside the printer. This stops quick changes in temperature. If the temperature changes fast, prints can bend or break. This is a big problem for large projects. Some materials, like ABS, Nylon, and ASA, need even heat to print well. Enclosures made from acrylic or polycarbonate keep heat in and block cold air. Good insulation keeps the inside warm. Fans and vents help control wetness and move bad air out.
Keeping the same temperature helps prints stick and look nice. It also makes less noise and keeps your work area safer.
Sensors, like thermistors, watch the heat of the nozzle, bed, and air. The printer uses heaters and fans to keep the right temperature. Here is a simple chart for common materials:
|
Material |
Nozzle Temp (°C) |
Bed Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|
|
PLA |
50–60 |
|
|
ABS |
230–250 |
90–110 |
|
PETG |
220–250 |
70–90 |
To get strong and correct prints, make sure your enclosure keeps these temperatures.
Material Requirements
Each material needs special settings. You must set your printer for the material you use. High-heat filaments like PEEK or PEKK need very careful heat control. If you use the wrong settings, prints can crack or get weak.
You can test your prints in different ways to check if they are good. These tests are:
-
Tensile tests: See how much pulling force your print can take.
-
Compressive tests: Check how much squishing your print can handle.
-
Flexural tests: Show how much your print bends before it breaks.
-
Hardness tests: Tell how tough the outside of your print is.
Tip: Change speed, layer height, and heat to get the best print for each material.
A good enclosure and the right settings let you use more types of filament. You waste less, save power, and get better prints. This helps your big projects and is better for the planet.
|
Correlation with Successful Outcomes in 3D Printing Projects |
|
|---|---|
|
Sustainable logistics reducing material wastage |
Helps the planet and makes projects work better |
|
Meeting environmental protection objectives/standards |
Makes projects succeed and helps more people use 3D printing |
|
Reduction in energy consumption and embodied carbon |
Is good for the earth and helps projects do well |
|
Recycling waste into new products |
Supports green goals and lowers harm to nature |
|
Minimizing production/environmental construction effects |
Cuts bad effects and makes projects greener |
|
Reducing human impact |
Keeps workers safe and healthy, helping the planet |
By watching heat and picking the right material, your large format 3D printer will do great on big jobs.
Software and Connectivity
Workflow Integration
You need software that links your big 3D printer to your work. Good software helps you watch jobs and control printers from anywhere. IoT lets your printer talk to cloud systems. You can see live data about the printer, like heat and material use. Tools like OctoPrint help you check many printers at once. For example, a team in Toronto used alerts to cut downtime by 15%. This means you finish big jobs faster and make fewer mistakes.
A strong 3D printing system should give you:
-
Easy printer links with other machines
-
Live checks and quick feedback
-
Auto schedules for fair workloads
-
Remote control for big teams
You also want your 3D printer to work with business systems. This helps you track parts, orders, and job status. You can find problems early and fix them fast. Live tracking and data help you use printers better and waste less.
User Interface
A simple user interface makes your work easier. You want controls that are easy to use. Good screens help you set up prints fast and make fewer mistakes. Some systems use cameras and smart computers to watch the nozzle and change settings right away. This keeps prints looking good and stops errors before they start.
Look for these things in the user interface:
-
Easy setup with clear steps
-
Live feedback and alerts
-
Simple camera use for watching prints
-
Fast access to print settings
Smart screens fix problems quickly. They can handle many issues at once and keep your prints going. You get better prints and spend less time fixing things.
Cost and Value
Industrial 3D Printers
When you look at industrial 3d printers, you see machines built for tough jobs and big projects. These printers handle large parts, strong materials, and long print times. You get more than just size. You get speed, accuracy, and less waste. Many companies now use industrial 3d printers for real products, not just for testing ideas.
- The 3D printing market grew by 26.8% in 2023. Experts expect it to reach $57.1 billion by 2028. This shows that more people trust and invest in industrial 3d printers.
- In a survey of over 700 engineers, 70% printed more parts last year. About 21% used 3D printing for finished products, not just models.
- 82% of users saved money with 3D printing. Almost half said they finished jobs faster than with old methods.
You can use industrial 3d printers for many things. People print furniture, tools, boat parts, and even parts for houses. These printers also help you try new designs without extra cost. You can change your plans and print again right away.
Industrial 3d printers give you flexibility and power for big projects. You can make complex shapes and save time.
Total Ownership
When you buy an industrial 3d printer, you need to think about more than just the price tag. You must look at the total cost of owning and running the machine. This includes setup, materials, repairs, and power use.
|
Cost Factor |
What to Watch For |
Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
|
Machine Price |
Upfront cost |
Affects your budget |
|
Material Costs |
Filament or resin prices |
Impacts each print |
|
Maintenance |
Repairs and spare parts |
Keeps printer running |
|
Labor Savings |
Automation and sensors |
Lowers staff time needed |
|
Energy Use |
Power for big prints |
Adds to long-term costs |
Industrial 3d printers often save you money in the long run. They use less material and need fewer workers. Automation and smart sensors help you spot problems early. You waste less and finish jobs faster. For big, complex parts, these printers beat old methods. You get lower costs, faster results, and more freedom to create.
User Feedback and Case Studies
Community Reviews
You can learn from others before buying a big 3D printer. Many people share their stories online. They post on forums, Reddit, and YouTube. These reviews show what is good and what is bad. Look for posts about print quality and setup. Some people share pictures of their large prints. You can see how printers work with big models.
Tip: Search for Sovol SV08 Max reviews. You will find honest thoughts on print size and speed.
Many users post guides and tips to fix problems. These help you solve common issues. People also talk about how easy it is to upgrade or repair. This helps you choose a printer that matches your skills.
Real-World Use
Case studies show how big 3D printers work in real jobs. Some engineers use them to make furniture models. Others print car parts or art. These stories show how printers handle different materials and sizes.
You can find case studies on company sites or maker groups. They tell you about print time, cost, and results. Some users print many things at once with a 500x500x500mm printer. This helps you know if a printer fits your needs.
|
Project Type |
Printer Used |
Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
|
Furniture Model |
Strong, smooth finish |
|
|
Car Prototype |
1000mm build volume |
Fast, accurate assembly |
|
Art Sculpture |
500x500x500mm model |
High detail, easy scaling |
Note: Real feedback shows what to expect. Always check new reviews and stories before you buy.
Here are 10 simple tips for choosing a big 3D printer:
- Know what your project needs
- See how big it can print
- Check if prints look good
- Make sure it uses the right materials
- Pick one that works well every time
- Compare how fast it prints
- Find smart and helpful features
- Look at the cover and work area
- Try the software and see if it connects
- Think about price and what people say
Make a list with these tips before you buy. Ask questions or share your stories about big 3D printers in the comments!
FAQ
What size build volume do you need for big projects?
You should look for a large format 3D printer with at least a 500x500x500mm build volume. This size lets you print furniture, sculptures, or prototypes in one piece. For even larger models, consider printers with a 1000mm or bigger build area.
Which materials work best with large format 3D printers?
You can use PLA, ABS, PETG, and sometimes nylon or carbon fiber. Always check your printer’s specs for material compatibility. Heated beds and high-temp nozzles help you print strong, warp-free parts for big projects.
How do you keep large prints from failing?
Use auto-bed leveling, filament sensors, and a strong frame.
Keep the print area warm with an enclosure.
Watch your printer during the first layers.
Sovol SV08 Max and similar models offer these features for better results.
Are industrial 3D printers worth the higher cost?
Industrial 3D printers cost more, but you get faster speeds, better reliability, and support for advanced materials. If you print large parts often or need top quality, the investment pays off. You also save time and reduce waste on big projects.




















