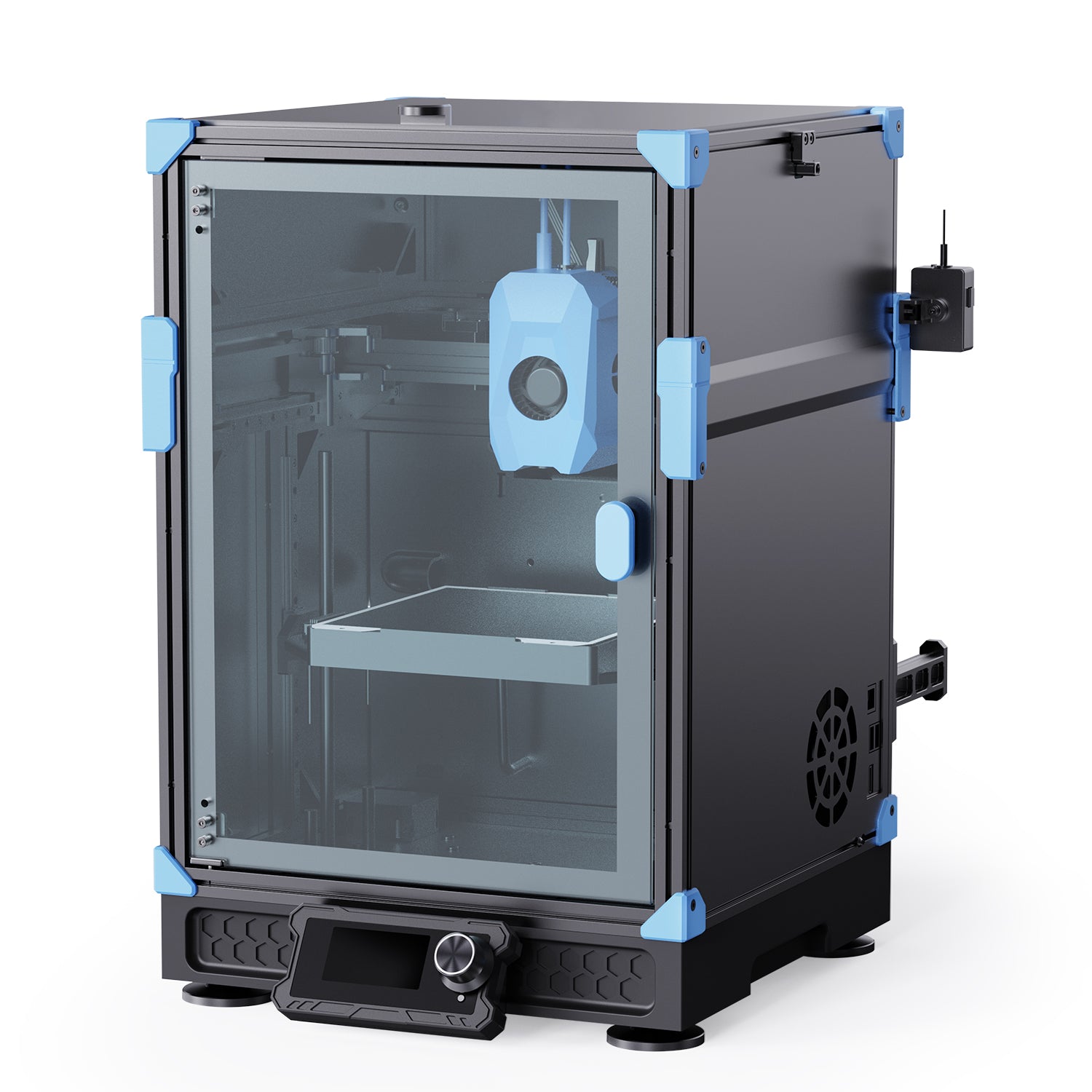
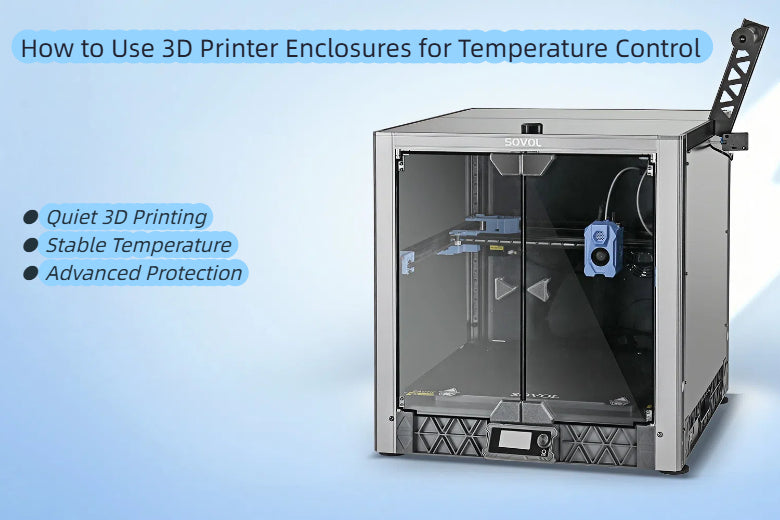
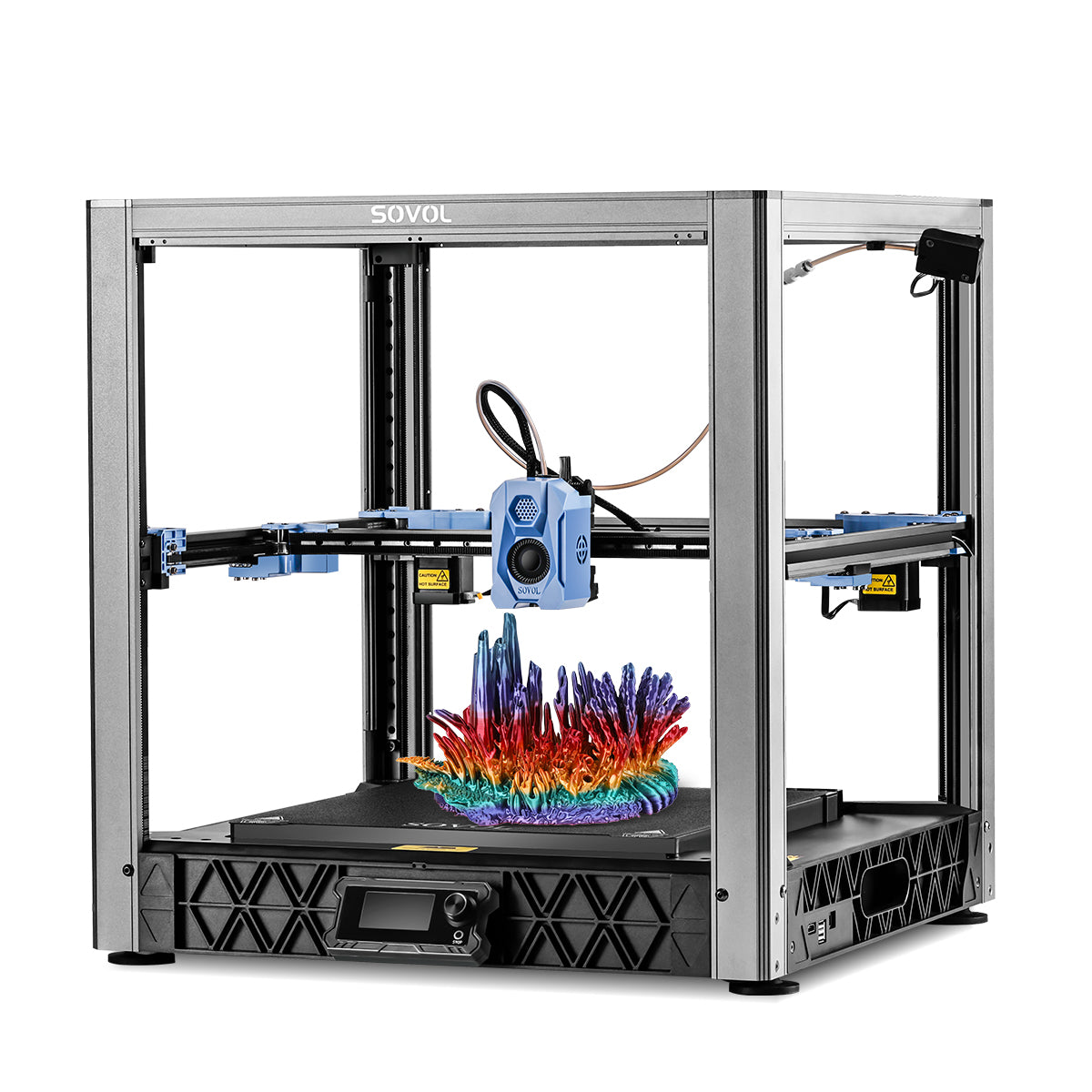
You want your 3d printer enclosures to make every print safer and more reliable. These enclosures help you keep a steady temperature, which prevents warping and cracking. They also protect you from fumes and accidental burns. When you use 3d printer enclosures, you improve print quality with less hassle.
Tip: Consistent temperature and clean air lead to better results and safer printing.
Key Takeaways
- Use a 3D printer enclosure to keep temperature steady and prevent warping or cracking in your prints.
- Choose enclosures with good ventilation and filters to protect yourself from harmful fumes and dust.
- Match the enclosure temperature to your filament type for the best print quality and fewer failures.
- Pick enclosures made from fire-resistant materials with easy access panels for safety and convenience.
- Maintain your enclosure by cleaning regularly, checking filters, and monitoring temperature for reliable printing.
3D Printer Enclosures Basics
Why Use an Enclosure
You want your 3D printer to work in the best possible conditions. 3D printer enclosures create a controlled space around your machine. This space keeps the temperature steady, which helps prevent warping and cracking during prints. When you use an enclosure, you also protect yourself from hot parts and moving components. The enclosure blocks dust and drafts, so your prints come out cleaner and smoother.
Here are some main reasons to use 3D printer enclosures:
- Maintain excellent thermal stability and insulation for consistent temperature.
- Improve safety by keeping you away from hot surfaces and trapping fumes.
- Block dust, drafts, and humidity, which can damage print quality.
- Reduce noise and vibration, making your workspace more comfortable.
- Support advanced materials that need higher or more stable temperatures.
Tip: If you print with materials like ABS or nylon, an enclosure helps you avoid failed prints due to temperature swings or moisture.
How Enclosures Work
3D printer enclosures use sturdy materials like polycarbonate, perspex, or foam insulation to create a sealed environment. The walls and doors keep heat inside and block outside air. This design lets you control the temperature and humidity, which is important for reliable printing. Scientific studies show that a well-designed enclosure can keep the temperature even across the whole print area. This helps your prints keep their shape and size, even with complex designs.
Most enclosures have features like:
- Clear panels for easy monitoring.
- Large doors or removable panels for access.
- Built-in fans or vents for airflow and fume control.
- Modular parts for easy upgrades or repairs.
You can add dehumidifiers or silica gel packs inside to keep humidity low. This protects your filament and improves print quality. By blocking dust and drafts, the enclosure keeps your workspace clean and your prints free from defects. You get more reliable results, even if the environment outside the enclosure changes.
Temperature Control
Stable Printing Environment
When you use a 3D printer enclosure, you create a stable printing environment. The enclosure traps heat and keeps the temperature around your printer steady. This steady temperature is important because it stops sudden changes that can ruin your prints. Open printers often face temperature swings and drafts from the room. These changes can cause your prints to cool too quickly, leading to warping or layer separation. Enclosures help you avoid these problems by blocking drafts and keeping the air inside warm and even.
A stable temperature inside the enclosure helps each layer of your print bond better. This means you get stronger, smoother prints with fewer defects.
Enclosed printers usually keep the internal temperature between 38°C and 42°C for materials like ABS. This range helps you avoid nozzle clogs and keeps the print surface at the right temperature. Some enclosures use heating modules or ceramic heaters to spread heat evenly. Even if your enclosure is not fully sealed, it still reduces drafts and keeps the temperature more stable than an open printer. For long or complex prints, this stability is even more important.
- You protect your prints from dust and sudden temperature changes.
- You reduce the risk of warping and layer separation.
- You get more reliable results, especially with advanced materials.
Material Considerations
Different filaments need different temperature settings inside your enclosure. ABS, PETG, and PLA each have their own ideal temperature ranges. Using the right temperature helps you get the best print quality and avoid common problems.
|
Filament |
Bed Temperature |
Notes |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
ABS |
Around 38-46°C |
Above 90°C |
Higher enclosure temps prevent warping; best in cold rooms. |
|
PETG |
20-40°C |
Around 70°C |
Handles wider temp range; enclosure keeps ambient temp steady. |
|
PLA |
20-30°C |
Varies (lower) |
Cooler temps avoid heat creep and jams; temps above 30°C can cause issues. |
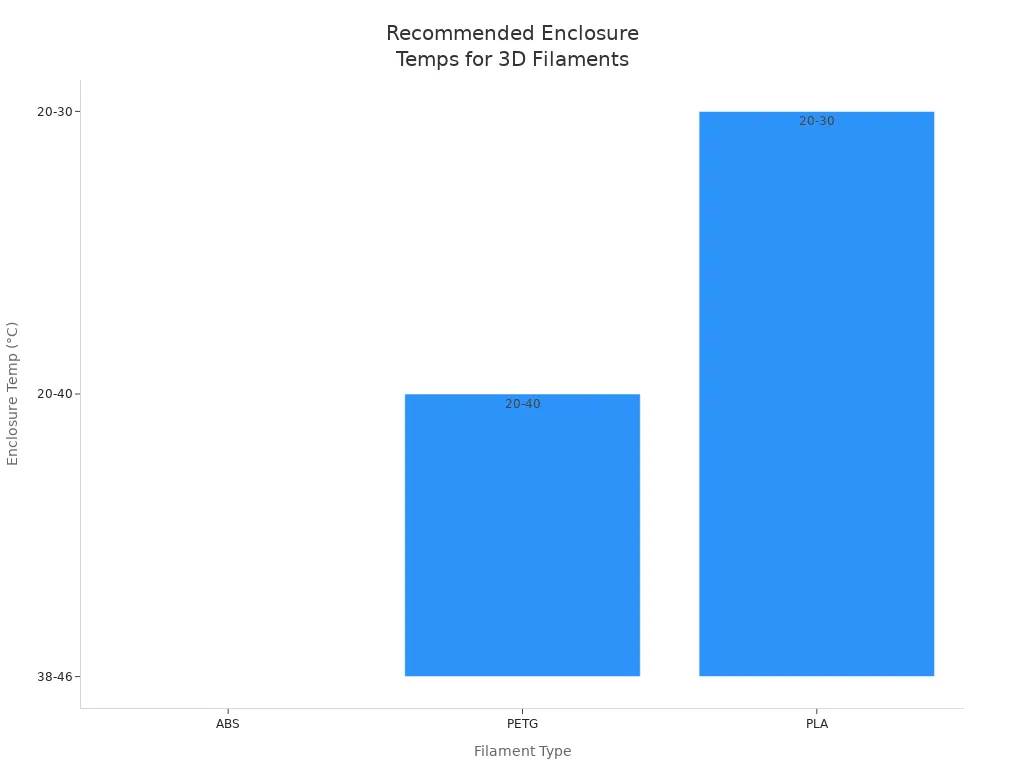
ABS and nylon need higher enclosure temperatures. These materials warp easily if the temperature drops or if there are drafts. Keeping the enclosure warm helps each layer stick together and stops the print from shrinking or cracking. PETG is less sensitive but still benefits from a steady temperature. PLA, on the other hand, works best at lower enclosure temperatures. If the enclosure gets too hot, PLA can clog the extruder or cause the print to stick too much to the bed.
Tip: If you print with PLA, open the enclosure door a little or use fans to keep the temperature below 30°C. This prevents heat creep and keeps your prints looking good.
Heated build plates work well with enclosures. The heated bed keeps the bottom of your print at the right temperature, while the enclosure keeps the air around the print warm. This combination helps your first layer stick better and reduces warping. You get stronger prints and better results, especially with materials like ABS.
- Always check the temperature inside your enclosure before you start printing.
- Adjust the enclosure temperature based on the filament you use.
- Use fans or vents to control heat when printing with PLA.
By managing the temperature inside your enclosure, you improve print quality and reduce failed prints. You also make it easier to work with advanced materials and complex designs.
Safety
Fire and Fume Risks
You need to think about safety every time you use a 3D printer enclosure. The heat from the printer, combined with electrical parts, can create fire risks if you do not follow proper steps. Always check that your enclosure uses fire-resistant materials and that all wires and electronics stay clear of moving parts. Good cable management helps prevent shorts and overheating. Never leave your printer running unattended for long periods.
3D printing also produces fumes and tiny particles. When you melt filaments like ABS or PLA, the process releases ultrafine particulates (UFPs) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). UFPs are so small that they can float in the air for up to two days. Breathing in these particles can harm your lungs and heart. VOCs can cause irritation and, over time, may damage your liver, kidneys, or nervous system. Some VOCs have even been linked to cancer. The longer you print, the more these risks increase.
Tip: Always use enclosures with built-in safety features, such as fire-resistant panels and clear emergency exits, to reduce fire hazards and protect your workspace.
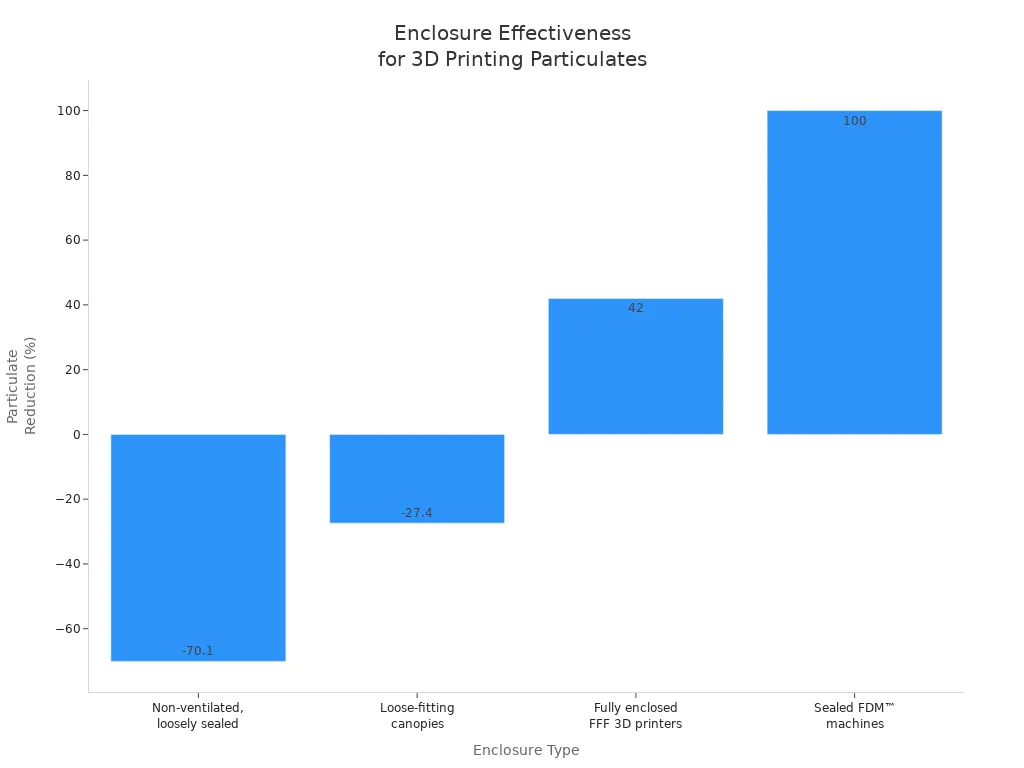
Enclosures help contain fumes and particulates, but not all designs work the same way. Some loose or open enclosures can actually make air quality worse by letting more particles escape into the room. Fully sealed enclosures with HEPA and activated carbon filters trap most harmful emissions inside. This keeps your workspace safer and helps you breathe easier.
|
Enclosure Type |
Filtration/Design Features |
Effectiveness on Particulates (%) |
Effectiveness on VOCs (%) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Non-ventilated, loosely sealed |
Side walls, no top/front, non-airtight doors |
Negative to low (-9.8% to -70.1%) |
Negative (increased VOCs) |
Particle concentrations increased in room during printing with PLA filament |
|
Loose-fitting canopies (large format) |
Custom-built canopies over build chambers |
Negative average (-27.4%) |
Negative average (-281%) |
Particle and TVOC concentrations elevated in room compared to inside enclosure |
|
Fully enclosed FFF 3D printers |
Internal recirculating HEPA and activated carbon filters |
Mixed (-18% effectiveness reported) |
Significant particle reduction; some VOCs increased inside enclosure after printing |
|
|
Ventilated enclosures (various AM types) |
HEPA and carbon filtration, ductless fume hoods |
Data insufficient for exact % |
Recommended |
Generally effective at reducing emissions; recommended engineering control |
|
Sealed FDM™ machines |
Sealed design with internal HEPA filter |
~100% reduction |
N/A |
Complete containment suggested; no significant particle increase in workroom during operation |
|
Post-printing exposure |
Doors opened after printing |
N/A |
TVOC spikes (~18 mg/m3) |
Acute gas-phase exposure risk when retrieving printed objects |
Ventilation and Filtration
You can improve air quality by using the right ventilation and filtration systems in your enclosure. HEPA and activated carbon filters remove most UFPs and VOCs before they reach your breathing space. Ductless filtering fume hoods and sealed enclosures with built-in filters work best. These systems capture harmful particles and gases at the source, making your workspace much safer.
To keep air quality high and reduce health risks, follow these best practices:
- Place fans near the top of the enclosure to move hot air and fumes out quickly.
- Use insulation to keep the temperature steady and prevent sudden changes that can affect print quality and air quality.
- Design your enclosure with large doors or sliding panels for easy cleaning and maintenance.
- Store filament inside the enclosure to protect it from dust and humidity, which also helps maintain air quality.
- Install sensors to monitor temperature, humidity, and fume levels for better safety and air quality management.
- Test airflow rates to make sure your enclosure provides enough fresh air for safe operation.
- Regularly clean and replace filters to keep your ventilation system working well.
- Choose commercial ventilation systems made for 3D printing for the best results.
- Always follow electrical safety codes and check grounding to prevent hazards.
Note: In schools and libraries, enclosures with advanced air filtration protect students and staff from harmful particles and fumes. They also reduce noise and prevent burns or injuries by keeping hot parts out of reach.
You should aim for at least six air changes per hour in your workspace to keep air quality at a safe level. Sealed enclosures with HEPA filters can almost completely remove particulates from the air. When you open the enclosure after printing, do it slowly and let the air clear before reaching in. This step helps avoid sudden spikes in VOCs and keeps air quality safe.
Enclosures play a big role in safety for everyone, especially in educational settings. They act as barriers against burns, moving parts, and harmful emissions. By choosing the right enclosure and maintaining good ventilation, you create a safer and healthier environment for 3D printing.
Choosing a 3D Print Enclosure
Key Features
When you select a 3d print enclosure, focus on features that improve safety, print quality, and ease of use. Look for these essentials:
- Insulation to keep temperature steady and reduce warping.
- Transparent or semi-transparent panels for easy monitoring.
- Good ventilation and filtration to remove fumes and keep electronics cool.
- Rigid, fire-resistant materials for safety.
- Damping rubber feet and plastic linear bearings to cut down on noise.
- Built-in LED lighting for clear visibility.
- Doors or removable panels for quick access and maintenance.
- Locking systems or barriers to protect users and pets.
Polycarbonate panels offer high impact resistance and can handle higher temperatures, making them ideal for industrial or high-temperature printing. Acrylic panels provide better clarity and cost less, which works well for home use with standard filaments. Always balance durability, safety, and visibility when choosing materials.
Tip: Avoid fully sealed enclosures without venting. Overheating can damage electronics and affect print quality.
Size and Access
The size of your enclosure matters. A larger enclosure helps you control temperature and humidity better, which leads to fewer print failures. You also get more space for your printer to move, reducing vibration and noise. Make sure the enclosure has enough room for cable management, tool storage, and future upgrades.
Easy access is important. Large doors, sliding panels, or removable sides make it simple to load filament, clean, or fix parts. Modular designs let you add or remove sections as your needs change.
DIY vs. Commercial Options
You can choose between building your own enclosure or buying a commercial model. DIY options often cost less and let you customize size and features. Use materials like MDF with insulation for better sound dampening. Commercial enclosures usually offer better safety, ventilation, and professional finishes. They often include advanced features like multi-stage filtration and temperature-triggered fans.
Think about your budget, the types of filaments you use, and how much time you want to spend on setup. Match the enclosure size to your printer and consider future needs. The right choice helps you print safely and get the best results.
Setup and Maintenance
Step-by-Step Setup
Setting up your 3D printer enclosure the right way helps you get the best results. Start by planning your enclosure. Think about the size, materials, and how your printer will fit inside. Gather all the panels, fasteners, and insulation you need. Assemble the frame and panels securely so the enclosure stays stable. Install ventilation fans and filters to control heat and remove fumes. Make sure you ground all electrical parts for safety. Place your printer inside, leaving enough space for airflow and easy access. Secure the doors or panels so you can reach your printer when needed. Before you start printing, test the enclosure for temperature stability and check that all electronics work well. Calibrate your printer’s stepper motors, especially the Z-axis, to improve print quality inside the enclosure.
Tip: Always check that your ventilation system works before starting a long print.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance keeps your enclosure working well and your prints looking great. Wipe down the enclosure surfaces every day to remove dust. Clean printheads and rollers each week. Check air filters often and replace them when they get dirty. Keep the temperature inside the enclosure steady, between 68°F and 78°F, and control humidity to prevent print defects. Inspect seals and doors for damage. Store your printer away from dust and moisture when not in use. Use a checklist or app to track your cleaning and maintenance schedule.
- Clean the fan system with compressed air, not water.
- Dry all parts before putting them back to avoid mold or corrosion.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific enclosure.
Troubleshooting
You may face issues like overheating or poor ventilation. If the enclosure gets too hot, your printer’s motors and electronics can overheat, causing print defects. Poor airflow can also lead to a buildup of fumes and humidity. Add fans or adjust your ventilation system to keep the temperature safe. Use temperature sensors to monitor heat levels. If you notice more fumes or dust, check and replace filters. Make sure doors and panels close tightly to keep the environment stable. For best results, combine temperature monitoring, fans, and filtration to keep your prints safe and high-quality.
Using a 3D printer enclosure gives you stable temperatures, cleaner prints, and a safer workspace. You prevent warping, block dust, and reduce fumes. For best results:
- Choose heat-resistant materials and fit the enclosure to your printer.
- Add ventilation, filters, and lighting for safety and visibility.
- Keep the enclosure closed during printing to limit airflows.
Hobbyists can try new materials. Educators protect students from burns and fumes. Professionals gain reliable, high-quality prints with less waste. Stay safe and enjoy better results with every print.
FAQ
How do I know if my 3D printer needs an enclosure?
You need an enclosure if you print with ABS, nylon, or other advanced filaments. You also benefit from one if you want to reduce fumes, noise, or dust. Enclosures help you get better results in rooms with drafts or temperature changes.
Can I build a DIY enclosure, or should I buy one?
You can build a DIY enclosure using materials like MDF, acrylic, or polycarbonate. Commercial enclosures offer better safety, filtration, and features. Choose DIY for customization and savings. Buy a commercial model for convenience and professional results.
What is the best way to ventilate my enclosure?
You should use a HEPA and activated carbon filter for best air quality. Place a fan near the top to move hot air and fumes out. Always check airflow with a sensor. Replace filters regularly to keep your workspace safe.
Which filaments benefit most from an enclosure?
|
Filament |
Needs Enclosure? |
Reason |
|---|---|---|
|
ABS |
Yes |
Prevents warping |
|
Nylon |
Yes |
Controls humidity |
|
PETG |
Sometimes |
Improves consistency |
|
PLA |
No/Optional |
Avoids overheating |
Tip: Use an enclosure for ABS and nylon. Keep it open or ventilated for PLA.