To choose 3d printer equipment that fits your needs, you must clarify your goals, understand different 3d printer types, and match features to your intended use. You need to consider your space, budget, and how the 3d technology will support your specific application. Many buyers underestimate funding, overlook hidden costs, or miss crucial details like software compatibility and maintenance needs. When you choose a 3d printer, you avoid common mistakes by planning for accessories, inspecting essential components, and ensuring support for your preferred materials. This process helps you make a confident and informed 3d purchase.
Key Takeaways
- Define your main goals before buying a 3D printer, such as prototyping, repairs, or production, to choose the right technology and features.
- Understand the differences between FDM, SLA, and SLS printers to match your needs for cost, print quality, strength, and material options.
- Consider key features like print quality, build volume, material compatibility, ease of use, and maintenance to ensure the printer fits your projects and skills.
- Plan your budget carefully by including not just the printer price but also materials, maintenance, and possible upgrades to avoid surprises.
- Check customer support and user communities to get help, share tips, and improve your 3D printing experience with reliable resources.
Define Your Goals

Main Use Cases
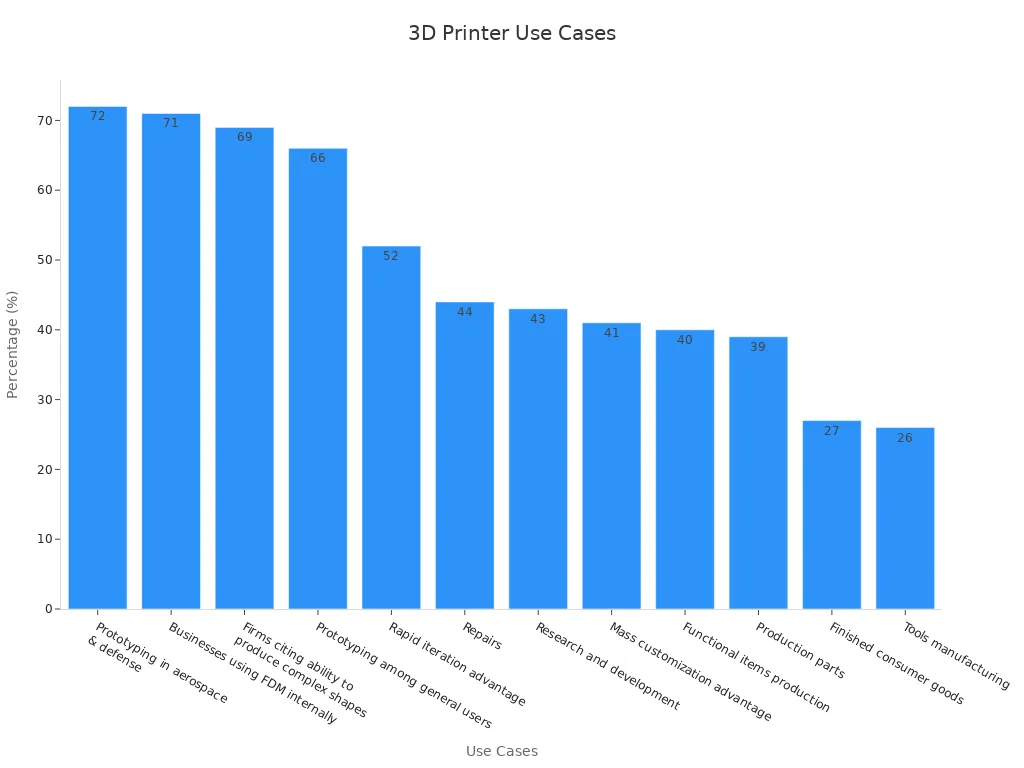
Before you select a 3d printer, you need to identify your main use cases. Most users focus on prototyping, especially in industries like aerospace, defense, and product design. Prototyping allows you to test ideas quickly and make changes before full production. In fact, 66% of users rely on 3d printers for prototyping, while 72% in aerospace and defense use them for the same purpose. Functional prototyping is also a top priority, as it helps you create working models that simulate real-world conditions. This process lets you check fit, form, and function before committing to expensive manufacturing.
You may also use a 3d printer for repairs, research, or producing end-use parts. The ability to produce complex shapes and rapid iteration gives you a competitive edge. Many businesses value functional prototyping because it supports innovation and reduces time to market. The chart below shows the most common use cases for 3d printers:
Future Needs
When you plan for the future, you should consider how your 3d printing needs might change. The 3d printing market is growing fast, with new trends like automation, AI integration, and sustainable materials shaping the industry. You may want a printer that supports advanced materials or offers features for functional prototyping as your projects become more complex. Businesses now look for printers that handle diverse applications and support eco-friendly practices.
|
Trend/Statistic |
Description |
Implication for Printer Choice |
|---|---|---|
|
Market Growth |
Demand for production-capable printers |
|
|
Automation & AI |
Integration for labor savings and quality control |
Preference for printers with smart features |
|
Specialized Materials |
New plastics, composites, and metals |
Need for versatile printers for functional prototyping |
|
Sustainability Focus |
Eco-friendly materials and processes |
Printers supporting sustainable practices preferred |
You should define your future goals early. If you expect to scale up production or shift from prototyping to manufacturing, choose a 3d printer that can grow with your needs. Functional prototyping will remain important as you develop new products and adapt to market changes.
3D Printing Types
FDM vs. Resin
When you explore 3d printing technology, you will encounter two main consumer options: FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) and resin-based methods like SLA (Stereolithography). FDM printers use thermoplastic filaments, melting and layering them to build objects. Resin printers use liquid photopolymers, curing each layer with light for high detail.
|
FDM Technology |
Resin-Based Methods (SLA, MSLA, DLP, PolyJet) |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Strength |
Generally stronger parts |
Typically less strong than FDM parts |
|
Cost-Effectiveness |
More cost-effective |
More expensive |
|
Surface Finish |
Rougher surface, porous parts |
Smooth, solid, non-porous parts |
|
Shape Complexity |
Limited complexity |
High complexity and fine details |
|
Material Versatility |
Wide range including fiber-infused composites |
Limited to photopolymers with improving toughness and heat resistance |
|
Application Suitability |
Functional, structural parts, outdoor use |
Microfluidics, dental, jewelry, small-scale manufacturing, sterile and liquid interaction applications |
You will find that FDM 3d printing technology offers fast prototyping and supports a wide range of 3d printing materials, including ABS, PLA, Nylon, PETG, and TPU. Resin printers excel in print quality, producing smooth surfaces and capturing fine details, which is ideal for dental, jewelry, and engineering prototypes. Both types deliver similar accuracy for many applications, with studies showing FDM can match SLA in dimensional accuracy for dental models.
Pros and Cons
You should compare FDM, SLA, and SLS 3d printing technology to match your needs. SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) stands out for industrial-grade parts and complex geometries, using nylon powder for superior mechanical properties. However, SLS printers come with higher costs and limited material options.
|
Technology |
Mechanical Properties |
Accuracy |
Material Compatibility |
Cost |
Application Suitability |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
SLS |
High |
Mainly nylon |
High |
Industrial, complex parts |
No supports needed |
|
|
SLA |
High strength, smooth finish |
High |
Wide resin range |
Medium-High |
Precise, functional parts |
Excellent detail |
|
FDM |
Lower strength, fast prototyping |
High |
Wide thermoplastics |
Low |
Rapid prototyping, cost-sensitive |
Struggles with fine details |
- FDM 3d printing technology gives you speed and affordability for prototyping, but struggles with fine details and surface finish.
- SLA provides excellent print quality and accuracy, but requires more maintenance and higher material costs.
- SLS delivers the best mechanical strength and design freedom, but you will face higher printer costs and limited 3d printing materials.
Note: Most 3d printers achieve about 0.2 mm accuracy, which suits many prototyping and functional part needs. However, you may need post-processing for the best surface finish or tight tolerances.
You should consider print speed, total cost, and the complexity of your designs when choosing a 3d printer. Each 3d printing technology offers unique strengths for different applications, from rapid prototyping to high-performance end-use parts.
Key Features
Print Quality
You should prioritize print quality when evaluating 3d printers. The resolution in 3d printing directly impacts the level of detail and surface finish you can achieve. SLA printers deliver the highest accuracy, with XY resolutions as fine as 10 microns and Z resolutions down to 10 microns. FDM printers typically offer XY resolutions between 100 and 500 microns, while SLS printers fall in the middle. The table below highlights these differences:
|
Technology |
XY Resolution (μm) |
Z Resolution (μm) |
|---|---|---|
|
FDM |
100-500 |
100-300 |
|
SLA |
10-100 |
10-50 |
|
SLS |
50-200 |
50-100 |
You will notice that higher resolution supports intricate designs and smooth surfaces. Experimental studies confirm that advanced 3d printing technology, such as PolyJet, achieves the best accuracy for complex models.
Build Volume
Build volume, or print capacity, determines the maximum size of objects you can produce. Larger build volumes let you print bigger parts or multiple items at once, which increases efficiency. You can match your printer’s build volume to your current and future project needs to avoid unnecessary upgrades. The table below shows typical build volumes for different printer types:
|
Printer Type |
Typical Build Volume (mm) |
Best For |
|---|---|---|
|
Standard 3D Printer |
200 x 200 x 200 |
Small models, toys |
|
500 x 500 x 500 Printer |
500 x 500 x 500 |
Furniture, prototypes, tools |
|
Extra Large-Format Printer |
1500 x 1500 x 2000 |
Industrial parts, automotive, molds |
Selecting a printer with flexible print capacity supports scalability and operational adaptability for diverse 3d projects.
Material Options
You need to consider the range of 3d printing materials your printer supports. Nylon offers strength and flexibility, while polycarbonate provides heat resistance and toughness. High-impact polystyrene and polyvinyl alcohol serve as support or specialty materials. ASA resists UV exposure, making it suitable for outdoor use. Metals and composites expand your application range but require advanced 3d printing technology. Fine-tuning material settings, such as layer thickness and infill density, helps you achieve the desired mechanical properties and print quality.
Ease of Use
Ease of use remains one of the key features to look for in any 3d printer. Many users face challenges with complex software and calibration. Print failures often result from user error or lack of training. Studies show that 69% of users want more reliable and affordable 3d printing technology. Improved training and user-friendly interfaces increase adoption rates and reduce frustration. Features like auto bed leveling and intuitive software make the 3d printing process smoother for both beginners and professionals.
Tip: Choose a printer with a strong knowledge base and active community support to boost your confidence and success rate.
Maintenance
Maintenance requirements differ across printer models and technologies. Predictive maintenance strategies use analytics and AI to optimize service schedules and reduce downtime. Maintenance costs include materials, labor, electricity, and ancillary services. These expenses vary based on the 3d printer’s design and the 3d printing technology it uses. Regular upkeep ensures consistent print quality and extends the lifespan of your equipment.
Practical Factors
Budget
You need to evaluate the total cost of ownership before you select a 3d printer. Budget considerations go beyond the initial price. You must account for materials, upgrades, and ongoing maintenance. Different pricing models, such as fixed-fee rentals or pay-per-build, affect your long-term expenses. High usage may justify owning a 3d printer, while occasional users might benefit from renting or using a platform. The table below compares key cost factors:
|
Practical Factor |
Description |
Impact on Cost |
|---|---|---|
|
Pricing Model |
Fixed-fee vs. pay-per-build |
Predictability vs. scalability |
|
Customization Effort |
User involvement in design and quality |
Higher utility, higher cost |
|
Product Complexity & Liability |
Failure rates and who bears liability |
Affects pricing and investment |
|
Usage Frequency |
How often you use the 3d printer |
Ownership vs. renting |
Popular 3d printer models like the Creality Ender 3 and Anycubic i3 Mega cost under $500, offering reliable performance for most users. However, you should also consider print speed, resolution, and upgradability, as these influence both your initial and future costs.
Space
You must assess your available space before purchasing a 3d printer. Some 3d printers have compact footprints, while others require dedicated workstations. Consider ventilation, noise, and accessibility for maintenance. A well-organized workspace improves safety and efficiency.
Support
Brand reputation and customer support play a crucial role in your 3d printing experience. High customer retention rates (40%-60% in the hobby market) indicate strong support and product satisfaction. Look for brands with high Net Promoter Scores (NPS above +50 is exceptional) and customer satisfaction scores above 80%. The table below highlights key support metrics:
|
Metric |
Definition |
Industry Benchmark |
|---|---|---|
|
Customer Retention |
Returning customers over time |
40%-60% |
|
Net Promoter Score |
Likelihood of recommending the brand |
+30 to +50 (good) |
|
Customer Satisfaction |
Happiness with product and service |
>80% |
Tip: Choose a 3d printer brand with responsive support and regular feedback channels to resolve issues quickly.
Community
A strong user community can help you solve problems, share tips, and access upgrades for your 3d printer. Online forums, social media groups, and local maker spaces offer valuable resources. Active communities often provide troubleshooting guides, firmware updates, and new 3d model files. You gain confidence and improve your skills by engaging with other users.
How to Choose a 3D Printer

Compare Models
When you choose 3d printer equipment, you need to compare models based on your specific goals. Start by identifying the main features that matter for your application, such as accuracy, build volume, and material compatibility. Research shows that industrial Multijet printers deliver higher accuracy and precision than many desktop models. However, recent improvements in desktop SLA and DLP printers have made them more affordable and suitable for clinical and professional use. You should also consider the software that comes with each printer.
A recent study compared 12 different 3d printers used in dentistry. The findings revealed that budget models like the Anycubic Photon and Elegoo Mars achieved accuracy levels similar to premium printers. This means you can find cost-effective options without sacrificing performance. The table below summarizes some key comparisons:
You should also pay attention to printing protocols. For example, oblique orientations and non-hollow horizontal settings often provide better accuracy for dental models. Always match the printer’s strengths to your intended use, whether you need high precision, speed, or cost savings.
Read Reviews
Before you choose a 3d printer, read user reviews and expert buyer’s guides. Reviews offer real-world insights into reliability, print quality, and ease of use. Look for feedback on machine uptime, customer support, and software updates. High customer satisfaction scores—such as an average rating of 4.5 out of 5—indicate strong performance and support.
You should also check for active user communities. These groups provide troubleshooting tips, firmware updates, and shared experiences that can help you solve problems quickly. Many users highlight the importance of features like heated beds, filament detection, and auto bed leveling. These features improve print quality and reduce failed prints.
Tip: Prioritize printers with comprehensive warranties and responsive support teams. This reduces downtime and repair costs.
Final Checklist
A structured checklist helps you choose 3d printer equipment that meets your needs and avoids costly mistakes. Use the following criteria to guide your decision:
|
Criterion Number |
Criterion Name |
Description Summary |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Application |
Define your intended use (prototypes, tooling, production parts) |
|
2 |
Accuracy & Surface Finish |
Required precision and quality impact cost and build time |
|
3 |
Choose a printer size that covers about 95% of your expected parts |
|
|
4 |
Material |
Consider physical properties, material changeover costs, and recalibration needs |
|
5 |
Color Capability |
Decide if you need color printing |
|
6 |
Build Speed |
Evaluate speed metrics and how multiple parts affect build time |
|
7 |
Maintenance |
Understand preventive maintenance and operator involvement |
|
8 |
Post-processing |
Assess finishing needs, space, tools, labor, and safety equipment |
|
9 |
Initial Investment |
Consider purchase price, installation, training, and warranty |
|
10 |
Recurring Costs |
Include consumables, maintenance, labor, repair, and capital costs over the printer’s lifespan |
You should also follow a maintenance schedule. Clean and lubricate your printer regularly, calibrate components, and inspect parts for safety. These steps extend the printer’s lifespan and improve print quality.
Steps to Choose 3D Printer
You can follow a clear, step-by-step process to choose a 3d printer that fits your goals:
-
Define Your Needs: Identify your main application, required accuracy, and preferred materials.
-
Research Technologies: Compare FFF, SLA, and SLS printers. FFF models offer affordability and ease of use, while SLA provides high precision and smooth finishes. SLS suits industrial and functional parts.
-
Evaluate Key Features: Check print volume, build chamber type, bed adhesion, layer resolution, extruder configuration, sensors, connectivity, software compatibility, and brand support.
-
Compare Models: Use tables and buyer’s guides to compare models side by side. Consider both technical specs and user feedback.
-
Check Operational Metrics: Review machine uptime (target 95% or higher), production turnaround time (6-8 hours per cycle), and cost savings (aim for 20% reduction over time).
-
Review Market Trends: Consider production efficiency, customer satisfaction, cost management, and innovation rate. Leading brands like Stratasys and 3D Systems often set industry benchmarks.
-
Use a Checklist: Go through your final checklist to ensure you have covered all critical factors.
-
Read Reviews and Community Feedback: Validate your choice with real-world experiences from other users.
-
Make Your Decision: Choose a 3d printer that aligns with your goals, budget, and operational needs.
Note: The best 3d printer for you balances performance, reliability, and cost. Use a structured approach to avoid common pitfalls and ensure long-term satisfaction.
You can confidently choose a 3d printer by following a clear process. Define your 3d goals, compare 3d technologies, and match each 3d printer’s features to your needs. Remember, customer support matters as much as print quality. Recent surveys show 98% positive feedback for SLS 3d printers, with most users praising fast, expert service and reliable 3d support:
- 86% rated service as "Awesome"
- 12% said "Just OK"
- Only 2% felt dissatisfied
Start your 3d journey today and unlock new possibilities with the right printer.
FAQ
What is the best 3D printer for beginners?
You should consider FDM printers like the Creality Ender 3 or Prusa Mini. These models offer easy setup, strong community support, and affordable pricing. You can learn basic 3D printing skills quickly with these reliable machines.
How often do I need to maintain my 3D printer?
You should perform basic maintenance after every 10–20 hours of printing. Clean the nozzle, check belts, and lubricate moving parts. Regular upkeep prevents print failures and extends your printer’s lifespan.
Tip: Set a reminder for monthly deep cleaning.
Can I print with multiple materials on one printer?
Many FDM printers support multiple materials, such as PLA, ABS, and TPU. Some advanced models offer dual extruders for multi-material printing. Always check your printer’s compatibility before purchasing new filaments.
How much does it cost to run a 3D printer?
You should budget for filament, electricity, and occasional replacement parts. Most users spend $10–$50 per month on materials. Electricity costs remain low for desktop models.
|
Expense Type |
Estimated Monthly Cost |
|---|---|
|
Filament |
$10–$50 |
|
Electricity |
$2–$5 |
|
Maintenance/Parts |
$5–$15 |

















Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.