When you look at PETG vs PLA for 3d printing, you find no single winner. PLA gives you easy prints and sharp details, but PETG brings more strength and flexibility. Your choice between PLA vs PETG depends on what you want from your 3d project. Some people value ease of use, while others want a filament that stands up to daily wear. PETG works well for items needing durability, while PLA fits quick, simple 3d printing jobs.

Key Takeaways
PLA is simple to use and prints sharp, bright details. This makes it good for beginners and for models that look nice. PETG is stronger and bends more without breaking. It works better for parts that need to handle stress, heat, or being outside. Use PLA for fast, easy projects and for shiny, colorful looks. Pick PETG if you want strong parts that last a long time. If you switch from PLA to PETG, you must change printer settings. You need higher temperatures and a prepared bed. Try both filaments to see which one works best for you. This will help you get better at 3D printing.
PETG vs PLA Overview

Key Differences
When you look at PETG and PLA, you see both are used a lot in 3d printing. They each have their own good points. PLA is made from things like cornstarch or sugarcane. It can break down in special compost places. PETG is a type of PET plastic that has been changed a bit. You cannot compost PETG, but you can recycle it.
You will find that PLA and PETG act differently when you print with them. PLA is simple to use and makes detailed models. You do not need a heated bed for PLA. It does not bend or twist much. PETG needs hotter settings and a heated bed. It can make thin strings, so you might need to change your printer settings.
If you want something strong and bendy, PETG is a smart pick. It does not break easily and can handle stress better than PLA. PLA is harder but can snap if you bend it. For things you use outside, PETG does better with sun and water. PLA does not last as long outside.
Tip: Pick PLA if you want easy and neat prints. Use PETG if you need strong parts that can be outside.
Quick Comparison Table
Here is a fast way to see how these two 3d printing filaments are different:
|
Aspect |
PLA |
PETG |
|---|---|---|
|
Origin |
Renewable (cornstarch, sugarcane) |
Petroleum-based (glycol-modified PET) |
|
Biodegradability |
Biodegradable (industrial composting) |
Not biodegradable, but recyclable |
|
Printability |
Easy, low temp, no heated bed |
Needs higher temp, heated bed, strings |
|
Tensile Strength |
Higher, but brittle |
Slightly lower, more flexible |
|
Flexibility |
Stiff, can crack |
Flexible, impact resistant |
|
Heat Resistance |
Lower (~60–65°C) |
Higher, better for hot environments |
|
UV/Water Resistance |
Low |
High |
|
Environmental Impact |
Lower carbon footprint |
More recyclable |
You can tell that both PETG and PLA are useful for 3d printing. Think about what your project needs before you choose. Each one gives you something special for your 3d prints.
Printability

PLA Printability
When you use PLA for 3d printing, you will notice its ease of use right away. PLA prints at lower temperatures, usually between 190°C and 240°C. You do not need a heated bed, which makes setup simple. PLA works well with most 3d printers and gives you sharp details. You can print PLA at average speeds of 50-70 mm/s, and some brands even allow speeds up to 150 mm/s. This means you finish your 3d projects faster. PLA also has fewer problems with stringing and oozing. Most users see clean prints with less mess between parts. However, you might see some issues like surface gloss changes or small bumps if the filament is not dry or the printer settings are off. Common defects include stringing, surface gloss inconsistency, and sometimes bubbles if the filament absorbs moisture.
PETG Printability
PETG filament needs more careful tuning when you use it for 3d printing. You must set the nozzle temperature higher, usually between 230°C and 250°C. The print bed should be heated to 70°C–90°C for good adhesion. PETG prints slower, with average speeds of 40-60 mm/s, because it needs time to cool and set. PETG tends to string more than PLA, so you need to adjust retraction settings and keep the filament dry. PETG sticks very well to the bed, which can sometimes damage the print surface if you are not careful. You should use a glue stick or spray to help with removal. PETG does not give as sharp corners or fine details as PLA, but it makes strong, flexible parts.
Beginner Friendliness
If you are new to 3d printing, PLA is the best choice for learning. PLA offers simple setup, faster print speeds, and fewer problems with stringing or bed adhesion. You can focus on learning your 3d printer without worrying about complex settings. PETG, on the other hand, can be tricky for beginners. You must watch out for stringing, strong bed adhesion, and the need for precise temperature control. Many people find PETG harder to master at first. For most beginners, PLA gives a smoother start and helps you build confidence in 3d printing.
Tip: Start with PLA to learn the basics of 3d printing. Move to PETG when you want stronger, more flexible parts and feel ready for more advanced tuning.
Strength & Durability
Strength
When you compare the strength of PLA and PETG, you see some clear differences. PLA has a higher average tensile strength than PETG. This means PLA can handle more pulling force before it breaks. You can see the numbers in the table below:
|
Material |
Average Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|
|
PETG |
54.9 ± 2.6 |
|
PLA |
PLA gives you strong prints, but it is also more brittle. If you bend or drop a PLA part, it can snap. PETG does not have the same high tensile strength, but it bends more before breaking. This makes PETG a better choice when you need superior strength in parts that must flex or take a hit.
Flexibility
Flexibility is another important property for 3D printing materials. PLA is stiff and does not bend much. PETG, on the other hand, is known for its flexibility and resilience. Some tests show PETG can stretch much more than PLA before breaking. In one test, PETG stretched over 100%, while PLA only reached about 12%. This means PETG can handle bending and twisting without snapping. You get more durability and resilience with PETG, especially for parts that move or need to absorb shock.
|
Property |
PLA |
PETG |
|---|---|---|
|
Breaking Elongation (%) |
12.2 ± 1.8 |
>100 |
Impact Resistance
Impact resistance tells you how well a material can handle sudden hits or drops. PETG stands out here. It has about double the impact strength of PLA. This makes PETG a top pick for parts that need to survive rough use or outdoor conditions. PLA can break if you drop it, but PETG absorbs the shock and keeps its shape. The chart below shows how PETG and PLA compare in different directions:
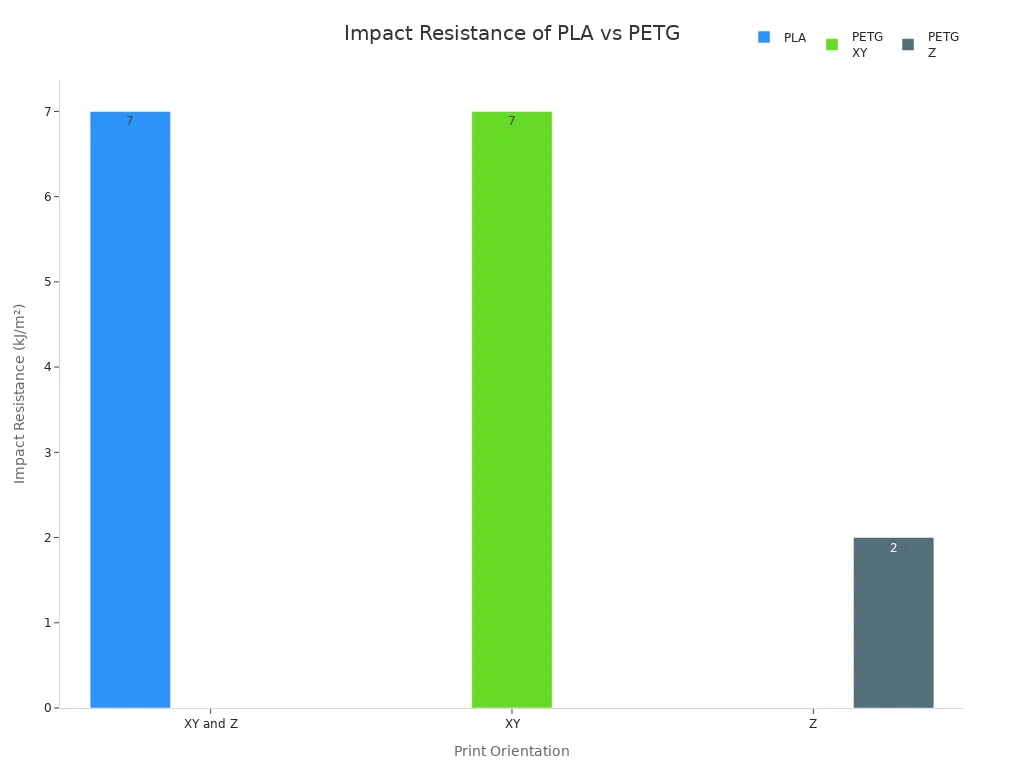
If you want durability and resilience in your prints, PETG offers superior strength for impact and flexibility. PLA works well for models and parts that do not need to bend or take a hit, but PETG is better for long-term use and tough environments.
Heat & Chemical Resistance
Heat Resistance
It is important to think about heat resistance when picking a 3D printing material. PLA and PETG both have limits for how much heat they can take. If it gets too hot, they start to get soft or lose their shape. PLA starts to change shape at lower heat. Most PLA prints will get soft at about 60°C. PETG can take more heat, up to 70–75°C if used all the time. This means PETG is better for things that get warm or sit in the sun.
Here is a table that shows the main heat properties for each material:
|
Material |
Maximum Continuous Use Temperature |
Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) |
Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
PETG |
70–75 °C |
80–85 °C |
70 °C |
|
PLA |
~60 °C (typical) |
~60 °C |
~60 °C (typical) |
You can see PETG has a higher heat deflection temperature than PLA. Some special PLA types, like annealed ePLA, can take more heat. Most regular PLA will not work well in hot places. The chart below shows how PETG, carbon fiber PETG, and annealed ePLA compare for heat: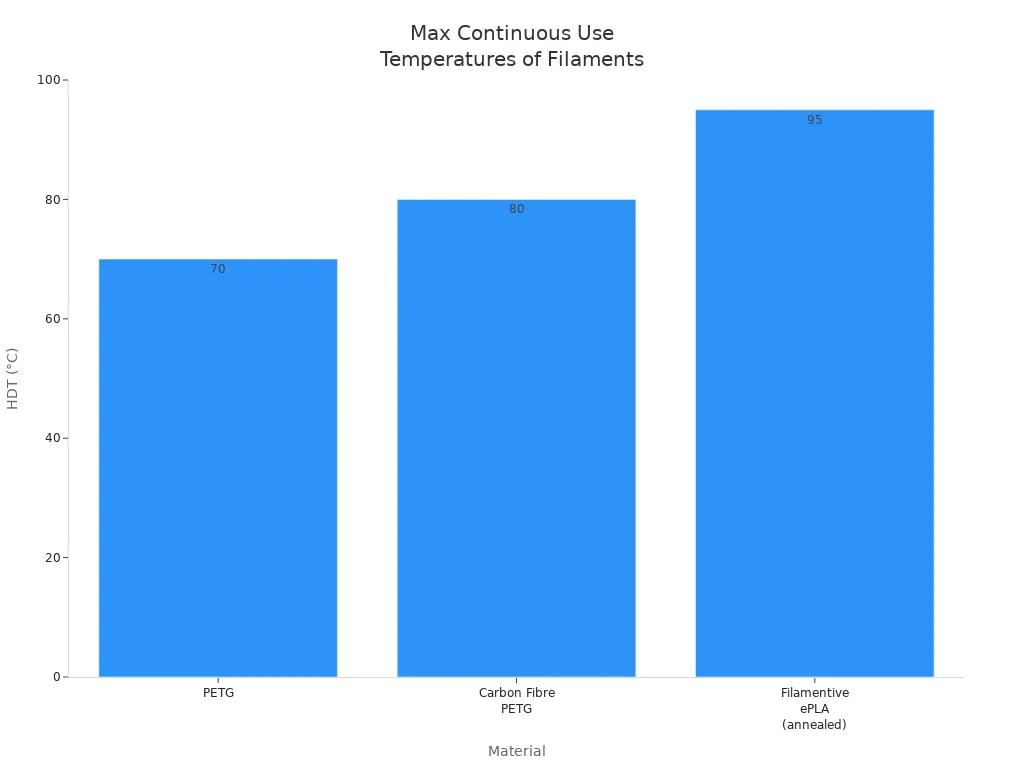
Tip: If your print will be in a hot car or near a window, PETG is usually a better choice.
Chemical Resistance
Chemical resistance is also important for 3D printing. You want your printed parts to last if they touch water, oils, or cleaning products. Both PETG and PLA do well with water. PETG is better when it comes to other chemicals. PETG can handle acids, bases, alcohols, and fuels much better than PLA. PLA is fine with water, salts, UV, and oils, but strong acids can break it down.
Here is a quick table to show how each material handles common chemicals:
|
Chemical |
PLA Resistance |
PETG Resistance |
|---|---|---|
|
Water |
High |
Very High |
|
Acids (e.g. HCl) |
Limited/Anecdotal |
Very High |
|
Bases |
Not specified |
Very High |
|
Alcohols |
Not specified |
High |
|
Fuels |
Not specified |
High |
|
Salts |
High |
Not specified |
|
UV |
High |
Not specified |
|
Oils |
High |
Very High |
If you want to use your prints outside or where they might touch chemicals, PETG gives better protection. PLA is good for indoor things that do not face tough conditions.
Surface Finish
PLA Filament Finish
When you print with PLA filament, you get a smooth and glossy surface. Many people like the way PLA looks right off the printer. You see sharp corners and fine details. This makes PLA a favorite for models, miniatures, and display pieces. The colors stay bright and even. You do not need to do much post-processing to get a nice finish.
Here are some common surface properties you notice with PLA:
- Smooth and shiny appearance
- Crisp edges and fine details
- Wide range of vibrant colors
If you want to sand or paint your print, PLA filament works well. You can use light sanding to remove small lines. Painting sticks to the surface easily. You get a clean look with little effort.
Tip: If you want the best detail and a polished look, choose PLA for your 3D prints.
PETG Finish
PETG filament gives you a different surface finish. You see a slight shine, but the surface feels more waxy or glossy compared to PLA. PETG does not show details as sharply. Sometimes, you notice small strings or tiny blobs on the print. These come from the flexible properties of PETG.
Here is what you can expect from PETG filament:
- Glossy but less crisp than PLA
- Slightly flexible surface
- More visible stringing or small imperfections
You can sand PETG, but it takes more work than PLA. Paint does not stick as well unless you prepare the surface. PETG filament works best for strong, functional parts where looks matter less than strength.
Note: If you need a tough part and do not mind a less perfect finish, PETG is a smart choice.
Cost & Availability
Price
When you shop for 3D printing filament, you want to know how much you will spend. PLA usually costs less than PETG. Most PLA filaments sell for $15 to $40 per kilogram. You often find good quality PLA around $20 to $25 per kilogram. PETG costs a bit more. You see PETG prices from $18 to $50 per kilogram, but most brands fall between $24 and $32 per kilogram. Some PETG brands cost even more if you want special features or recycled material.
Here are some examples of PETG prices per kilogram:
- Sovol PETG Filament: about $29.00
- Polar Filament PETG: about $31.66
- Polymaker PETG: about $32.48
- Atomic PETG: about $32.98
- Prusament PETG: about $33.64
- Coex 3D PETG: about $35.69
- 3DxTech PETG: about $36.00
- American Filament PCTG: about $36.48
- 3D Fuel PCTG: about $39.90
- GreenGate 3D Recycled PETG: about $44.98
- ProtoPasta PETG (500g spool): about $59.99
You can see that PLA is the most common and affordable filament. PETG costs more because it offers extra strength and flexibility.
Tip: If you want to save money or print many models, PLA gives you the best value.
Color Options
You have many choices when it comes to color and finish. PLA stands out for its wide range of specialty colors and finishes. You can find PLA in matte, silk, glow-in-the-dark, and even color-changing options. Manufacturers add special pigments and additives to create these effects. This means you can print models that look shiny, soft, or even metallic.
PETG usually comes in standard colors like black, white, red, or blue. Most PETG filaments have a glossy finish. You do not see as many specialty finishes for PETG. If you want a unique look, PLA gives you more options.
|
Feature |
PLA |
PETG |
|---|---|---|
|
Color Variety |
Very wide, many finishes |
Standard, glossy |
|
Specialty Looks |
Matte, silk, metallic, etc |
Rare |
Note: Choose PLA if you want bright colors or special finishes. PETG works best for strong, simple parts where color is less important.
Use Cases
PLA vs PETG Applications
You can use both PLA and PETG for many 3d printing projects, but each one shines in different areas. If you want to print decorative items or simple models, PLA is a great choice. It is easy to use and gives you bright colors and smooth finishes. Many hobbyists pick PLA for display pieces, educational models, and quick prototypes.
PETG works well when you need strength and durability. You often see PETG used for mechanical parts, robotics, and even medical braces. This 3d filament is safe for skin and food, so you can use it for items like bottles or covers. PETG also resists chemicals and holds up under stress, making it a smart pick for guards, electronics, and artistic prints like bracelets.
-
Common uses for PLA:
- Decorative models
- Prototypes
- Educational projects
-
Common uses for PETG:
- Functional parts
- Mechanical components
- Medical and food-safe items
Tip: Choose PLA for easy, colorful prints. Pick PETG when you need strong, lasting 3d parts.
Outdoor Use
If you plan to use your 3d prints outside, you need to think about sunlight, rain, and heat. PLA does not last long outdoors. Sunlight and moisture can make it fade and break down. It also softens in hot weather, so it is not the best choice for outdoor projects.
PETG stands up better to outdoor conditions. It resists UV rays and moisture, so it keeps its shape and color longer than PLA. PETG also has a higher heat resistance, so it will not warp as quickly in the sun. Some users find that PETG prints can last about a year outside before they start to get stiff or brittle, especially if you use clear filament. You can make PETG last even longer by using opaque colors or adding a UV-protective coating.
Note: For outdoor 3d projects, PETG is usually the better material. PLA works best indoors or for short-term outdoor use.
Miniatures & Prototypes
When you want to print miniatures or prototypes, you need sharp details and a nice finish. PLA gives you smooth surfaces and bright colors, which makes it perfect for small models and display pieces. It is easy to print and does not need much tuning, so you get great results even if you are new to 3d printing.
PETG is better for functional parts or prototypes that need to handle stress or heat. It does not show details as well as PLA, but it gives you more strength and flexibility. If your prototype needs to work in real-world conditions, PETG is a good choice.
|
Feature |
PLA |
PETG |
|---|---|---|
|
Printability |
Needs tuning |
|
|
Surface Finish |
Smooth, colorful |
Glossy, less detail |
|
Best For |
Miniatures, models |
Functional parts |
If you want the best look for your miniatures, use PLA. For strong prototypes or working parts, try PETG.
Choosing Between PLA and PETG
Which to Choose?
You want to pick the best filament for your project. To do this, you should think about a few key things. Each material has good and bad sides. The right choice depends on what you need your print to do.
Here is a table that helps you compare the main points:
|
Decision Factor |
PLA Characteristics |
PETG Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
|
Strength & Durability |
More brittle, good for decorative and low-stress use |
Superior strength, impact resistance, ideal for functional parts |
|
Environmental Impact |
Biodegradable, eco-friendly |
Recyclable, longer lifespan offsets environmental impact |
|
Aesthetic Quality |
Smooth finish, wide color range, less stringing |
Glossy, prone to stringing, may need post-processing |
|
Printability & Ease |
Easier to print, minimal warping, beginner-friendly |
Needs higher temps, more challenging, stringing issues |
|
Heat Resistance |
Lower heat resistance |
Higher thermal stability, suitable for outdoor use |
|
Printer Compatibility |
Works with most printers, lower temp requirements |
Needs heated bed, higher temp, printer must support PETG |
|
User Experience |
Ideal for beginners and decorative projects |
Better for experienced users needing durable parts |
|
Project Suitability |
Prototypes, models, eco-conscious projects |
Mechanical parts, outdoor exposure, functional applications |
Ask yourself these questions before you choose:
- Do you need your print to be strong and bendy? PETG is best for parts that take stress or go outside.
- Is your project just for looks or display? PLA gives a smooth finish and bright colors.
- Does your printer have a heated bed and get hot enough? PETG needs both of these.
- Are you new to 3D printing? PLA is easier and helps you learn.
- Do you care about the environment? PLA breaks down, but PETG can be recycled and lasts longer.
Tip: If you want to print a model or test piece, start with PLA. If you need a tough part for daily use, PETG is a better fit.
You can also check this quick table:
|
Feature |
PLA |
PETG |
|---|---|---|
|
Ease of Use |
Very easy, beginner-friendly |
Moderate, skill-dependent |
|
Durability |
Fragile |
Robust |
|
Thermal Stability |
Limited |
Reliable |
|
Cost |
Economical |
Premium |
Many people who have more experience like PETG for strong builds. If you want to try new things, print with both and see which works best for you.
Tips for Switching
If you want to change from PLA to PETG, you need to adjust your setup. Many people make mistakes when they switch, but you can avoid problems if you follow some steps.
- Clean your print bed well. Use dish soap and water, then wipe with alcohol. This gets rid of old PLA that can mess up PETG sticking.
- Put a glue stick or Windex on the bed. This helps PETG stick while printing and makes it easier to take off the finished part.
- Change your Z-offset. Raise it by about 0.2mm for a better first layer with PETG.
- Lower your cooling fan speed at the start. PETG prints rough if it cools too fast.
- Use different print surfaces for each material. If you have a spring steel sheet, print PLA on one side and PETG on the other.
- Clean your nozzle when you switch back to PLA. Run cleaning filament or do a cold pull to get out sticky PETG.
- Try a silicone sock on your nozzle. This keeps the heat steady and stops filament from sticking.
- Watch your extrusion rate. If your extruder skips, lower the max volumetric rate for PETG.
Here is a table that shows common mistakes and how to fix them:
|
Common Mistake |
Cause (PETG) |
How to Avoid / Fix (PETG) |
|---|---|---|
|
Stringing and Oozing |
High viscosity, long molten state |
Increase retraction, lower temp by 5-10°C, dry filament |
|
Warping, Poor Adhesion |
Warping on large prints |
Heated bed at 70-90°C, low fan speed, use glue stick |
|
Layer Adhesion Issues |
Layers may not bond well |
Print at 220-250°C, slow speed, lower fan speed |
|
Brittle Prints |
Printed too cold, moisture |
Raise temp, dry filament, store dry |
|
Overheating and Blobs |
Excess heat |
Lower temp, decrease flow rate, increase cooling fan speed |
Note: Take your time when changing materials. Small changes in settings can make a big difference in how your print turns out.
If you follow these tips, you will get better prints and avoid common problems. You will also learn more about your printer and how each filament works.
Each filament has its own special strengths. PETG is strong and can bend without breaking. It also does not get damaged by water or chemicals. PLA is much easier to print with. It is safe for use in schools and makes detailed models look great.
You should try both materials to see which one you like. Think about what you need most, like strength or easy printing. Testing different filaments helps every 3D printer user learn what works best.
FAQ
What is the main difference between PLA and PETG?
PLA prints easily and gives you sharp details. PETG offers more strength and flexibility. PLA works best for simple models. PETG suits parts that need to last longer or handle stress.
Can you use PLA and PETG on the same 3D printer?
Yes, you can use both on most 3D printers. Make sure your printer has a heated bed for PETG. Clean the nozzle and bed when switching materials for the best results.
Is PETG food safe?
PETG is often labeled food safe. You should check the manufacturer’s details. Always use a clean, stainless steel nozzle and avoid coloring agents if you want to print food containers.
Does PLA or PETG last longer outdoors?
PETG lasts longer outdoors. It resists sunlight and water better than PLA. PLA can fade and break down in the sun or rain. For outdoor projects, PETG is the better choice.
How do you reduce stringing with PETG?
You can lower stringing by drying your filament, increasing retraction settings, and lowering the print temperature. Try a small test print to find the best settings for your printer.