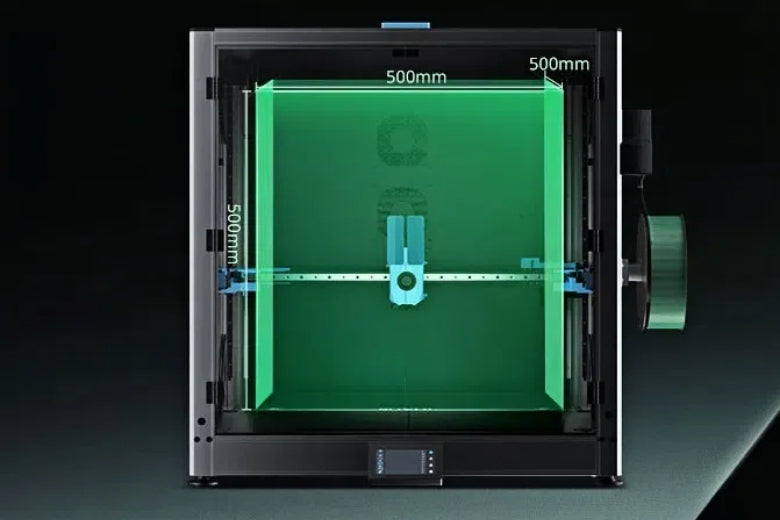
Large-scale 3D printing now drives a major shift in the construction industry. Builders and manufacturers use digital, automated processes to create complex structures with unmatched speed. The Sovol SV08 Max, with its impressive build volume, shows how these machines handle ambitious projects. In the construction industry, housing projects once took months, but 3D printing can finish them in just a day. This technology delivers cost-effective solutions, reduces waste, and meets the rising demand for customizable housing. The table below highlights the impact of large-scale 3D printing on construction and manufacturing.
|
Statistic / Example |
Value / Description |
|---|---|
|
Average duration of custom home projects |
4 months or more |
|
Percentage of mega construction jobs running over deadline |
98% |
|
Average delay over estimated deadlines in mega projects |
30% |
|
Projected 3D printing construction market size by 2024 |
$1.5 billion |
|
Compound annual growth rate (2019-2024) of 3D printing construction market |
245.9% |
|
Apis Cor's 3D printed house completion time |
24 hours |
|
Yingchuang Building Technique's projects |
5-story apartment complex and 1,100-square-meter home completed via 3D printing |
Key Takeaways
- Large-scale 3D printers like the Sovol SV08 Max speed up construction and manufacturing, cutting project times from months to days.
- This technology lowers costs by reducing material waste, labor needs, and expensive tooling, making projects more affordable.
- 3D printing allows for flexible, custom designs that traditional methods cannot easily achieve, supporting unique and complex structures.
- Sustainability improves as 3D printing uses only needed materials, recycles waste, and reduces energy and CO2 emissions.
- Despite challenges like material limits and regulations, ongoing advances promise faster, safer, and more eco-friendly building solutions.
Large-Scale 3D Printing

Key Features
Large-scale 3D printing stands at the forefront of innovation in manufacturing and construction. These advanced machines deliver the ability to create 3D printed structures with dimensions and complexity that traditional methods cannot match. The Sovol SV08 Max, for example, offers a massive 500×500×500 mm build volume. This capacity allows users to print large-scale structures in a single piece, reducing assembly time and improving overall quality.
Key features of large-scale 3D printing systems include:
- High Build Volume: Machines like the Sovol SV08 Max can produce objects up to half a meter in each dimension. This enables the creation of furniture, architectural components, and even entire sections of buildings.
- Material Compatibility: These printers support a wide range of materials, such as PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU, and advanced composites. Each material offers unique mechanical properties, making them suitable for different construction and manufacturing needs.
|
Material |
Tensile Strength (psi) |
Elongation at Break (%) |
Glass Transition Temp. (°C) |
Printing Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
PLA |
~7,250 |
6 |
60-65 |
200-220 |
|
ABS |
~4,600 |
20 |
~105 |
220-250 |
|
PETG |
~7,250 |
20-30 |
85 |
220-260 |
- High-Flow Extruders and Automation: Advanced extruders and automated calibration systems ensure consistent quality and faster print speeds. The Sovol SV08 Max reaches up to 700 mm/s, with acceleration rates of 40,000 mm/s², making it one of the fastest in its class.
- Precision and Reliability: Features like CoreXY motion systems, dual linear actuators, and AI-based real-time monitoring deliver high accuracy and reduce print failures.
- Software and Control: Modern printers use sophisticated software for process planning, print orientation, and defect detection. These tools optimize structural strength and minimize waste.
Note: Large-scale 3D printing technology also supports innovative construction methods, such as 3D printing concrete formworks and monolithic on-site structures. These approaches streamline the building process and open new possibilities for architectural design.
Benefits
The benefits of large-scale 3D printing extend across manufacturing and construction. These advantages drive the rapid adoption of 3D printing technology in both industries.
- Efficiency and Speed: Large-scale 3D printing reduces production time by up to 50%. For example, the Sovol SV08 Max can print detailed models or functional parts in days rather than weeks. In construction, 3D printed structures like houses can be completed in just 24 hours.
- Cost Savings: Companies report up to 75% savings in sand casting costs and 30-40% reductions in material waste and labor expenses. The table below compares improvements over traditional methods:
|
Metric |
Large-Scale 3D Printing Improvement |
Traditional Methods |
|---|---|---|
|
Production Speed |
Up to 50% reduction in time |
Longer production cycles |
|
Cost Savings |
Up to 75% in sand casting |
Higher costs |
|
Cost Variation |
26% based on print orientation |
N/A |
- Design Flexibility: 3D printing technology allows for complex geometries and custom designs. Architects and engineers can create unique 3D printed structures without the limitations of molds or traditional assembly. The Sovol SV08 Max supports mass customization, as seen in projects like the Nanjing Happy Valley East Gate.
- Sustainability: Large-scale 3D printing reduces waste by using only the material needed for each part. Many companies now use recyclable or bio-derived materials to meet sustainability goals. The technology also lowers transportation needs by enabling on-site production.
|
Statistic Description |
Data/Value |
|---|---|
|
18% to 27% annually |
|
|
Projected market value by 2026 |
$37.2 billion |
|
Percentage using 3D printing to reduce manufacturing waste |
22% |
|
Percentage expecting sustainability improvements |
38% |
|
Percentage reporting substantial cost savings from 3D printing |
82% |
|
Percentage emphasizing need for more affordable technology |
69% |
|
Market share of metal materials in 3D printing |
Over 48% of global revenue |
|
CAGR of ceramics market in 2022 |
23.3% |
|
Industrial printers' share of global 3D printer sales |
Over 76% |
|
Percentage of businesses printing more parts in 2023 vs 2022 |
70% |
|
Percentage citing cost as main barrier to adoption |
55% |
|
Percentage wanting to increase investment in 3D printing |
61% |
|
Global 3D printing market size in 2023 |
$20.37 billion |
|
CAGR of 3D printing revenue growth (2023-2024) |
17.2% to 19.8% |
|
Predicted CAGR of 3D printing market (2022-2027) |
23% |
|
North American 3D printing market size by 2032 |
$16.59 billion |
|
Percentage optimistic about 3D printing's future role |
58% |
-
Real-World Impact: The Sovol SV08 Max demonstrates these benefits in practice. In education, students print anatomical models in two days. In retail, businesses create large displays like the Giant Golden Dragon at Sydney Airport. In construction, 3D printed structures reduce labor and speed up project timelines.
Tip: Companies that adopt large-scale 3D printing gain a competitive edge by delivering projects faster, reducing costs, and offering greater design flexibility.
The benefits of 3D printing continue to grow as technology advances. With improved material compatibility, automation, and precision, large-scale 3D printing is transforming how industries approach construction and manufacturing. The focus on sustainability and cost-effective solutions ensures that 3D printed structures will play a central role in the future of building and production.
Manufacturing
Rapid Prototyping
Large-scale 3D printing is changing the way companies approach rapid prototyping in both manufacturing and construction. With machines like the Sovol SV08 Max, engineers can create full-size prototypes in a fraction of the time needed for traditional methods. In architecture, 3D printing technology reduces model-making time from weeks to just hours. This speed allows architects to test ideas quickly and share them with clients, improving communication and project outcomes. Boeing used large-scale 3D printing to produce a rotor system for the Apache AH-64 helicopter. The process took only nine hours, compared to a year with forging. This dramatic time reduction helps teams move from concept to testing much faster.
Manufacturers also benefit from lower tooling costs. Traditional prototyping often requires expensive molds and tools. With additive manufacturing, companies print parts directly from digital designs, eliminating many setup steps. This approach supports on-site customization and lets teams iterate designs rapidly.
Product Development
Product development in manufacturing and construction has become more efficient with big 3D printers. Companies like ARaymond cut development time from eight weeks to just three days by using advanced 3D printing. This 94% reduction in development time means products reach the market faster. The table below shows how other companies have improved their processes:
|
Company/Source |
Reduction in Tooling/Development Time |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Graco Inc. |
Up to 75% |
Faster prototyping for paint spraying equipment |
|
Various Users |
43% to 96% |
Faster prototyping in aerospace, automotive, and education |
Additive manufacturing also brings new levels of customization and supply chain resilience:
- Companies like ZF Friedrichshafen AG report up to 50% shorter lead times.
- On-demand production reduces inventory and storage costs.
- Manufacturers adapt quickly to market changes, improving operational agility.
- Localized production lowers transportation costs and supports sustainability in construction.
- Digital integration and AI-driven quality control improve part accuracy.
Big 3D printers like the Sovol SV08 Max help manufacturers and construction teams respond to changing demands, reduce waste, and deliver better products in less time.
Construction Industry
3D Printing in Construction
The construction industry faces urgent challenges, including the global housing crisis and the need for affordable housing. 3D printing in construction offers a powerful solution. Companies now use advanced printers to build homes, schools, and offices faster than ever. For example, a 140 m² house in Angola was 3D-printed in just 30 hours. Workers installed water and electrical pipes at the same time, showing how automation reduces manual labor. Large-scale printers can complete buildings in as little as 28 hours, while traditional construction often takes weeks or months.
3D printing in construction automates many steps. This reduces the need for large teams and lowers labor costs. Organizations like CEMEX and projects such as TECLA in Italy and the Eindhoven University of Technology’s 3D printed concrete home in the Netherlands show how this technology delivers both speed and affordability. These projects help address the affordable housing crisis by making homes available quickly and at lower cost.
The Sovol SV08 Max, with its large build volume and material compatibility, demonstrates how big 3D printers can create complex 3D printed structures. Builders use these machines to print walls, floors, and even entire sections of buildings. This approach supports new housing solutions and helps the construction industry respond to the global housing crisis.
Efficiency and Cost
3D printing in construction improves efficiency and reduces costs. Automation allows teams to finish projects in days instead of months. Integration of robotics with additive manufacturing has led to a 46% reduction in time-to-market and a 25% improvement in build accuracy. These improvements help the construction industry deliver more housing in less time.
Cost analysis reports highlight several key points:
- Initial equipment costs range from $49,000 to $800,000, depending on the printer and project size.
- 3D printing in construction mainly reduces costs for wall framing, while other components may still be expensive.
- Labor costs drop because fewer workers are needed on-site.
- Material waste decreases, but transportation and setup costs remain important factors.
- Speed advantages are clear, but setup and calibration can affect overall efficiency.
- Challenges include building code compliance and appraisal uncertainties.
A table below summarizes logistics and cost findings from recent studies:
|
Aspect |
Onsite 3D Printing |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Cost Drivers |
Higher warehousing/assembly |
Lower warehousing/assembly |
|
Transportation Cost |
Lower for small projects |
Lower for large projects |
|
Non-value Added Cost |
284.26 €/tonne |
199.05 €/tonne |
|
Cost-effectiveness |
Capital intensive |
Better for large projects |
|
Feasibility |
Small-scale |
Large-scale |
3D printing in construction also reduces material waste. Studies show that 3D printed structures use only the amount of material needed, which lowers costs and supports affordable housing. Builders can print homes on-site, reducing transportation costs and making it easier to deliver housing solutions in remote areas.
Sustainability and Safety
Sustainability and safety have become top priorities in the construction industry. 3D printing in construction supports these goals in several ways:
- 3D printing in construction can reduce concrete usage by up to 70% compared to traditional methods.
- CO2 emissions from construction projects can drop by as much as 32% when using 3D printing techniques.
- Builders use recycled materials, such as brick aggregates and even recycled gloves, to create new construction materials. This promotes circularity and reduces embodied carbon.
- Life Cycle Assessments show that 3D printing in construction reduces the need for formwork and optimizes material use.
- The use of coarser aggregates in 3D construction printing mixtures can lower cement consumption, which is the most environmentally impactful raw material.
3D printing in construction also improves safety. Automation reduces the need for labor-intensive tasks, lowering the risk of accidents. Workers spend less time on dangerous jobs, and precise designs make construction sites safer. The technology allows for the creation of complex shapes that traditional methods cannot achieve, improving both efficiency and safety.
The market for 3D printing in construction is growing rapidly. The table below shows recent market forecasts:
|
Source |
Base Year Market Size (USD Billion) |
Forecast Year |
Forecast Market Size (USD Billion) |
CAGR (%) |
Forecast Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Straits Research (2025) |
2033 |
93.67 |
54.39 |
2025-2033 |
|
|
GM Insights (2023) |
2032 |
N/A |
59.6 |
2024-2032 |
|
|
InsightAce Analytic |
2034 |
1231.6 |
59.2 |
2025-2034 |
|
|
Straits Research (2024) |
1.90 |
2033 |
93.67 |
54.23 |
2025-2033 |
These numbers show strong growth and future potential for 3D construction printing. As the construction industry adopts more 3D printing in construction, builders can deliver affordable housing, address the global housing crisis, and support sustainable construction. The Sovol SV08 Max and similar machines will continue to play a key role in shaping the future of housing and construction.
Real-World Application
Case Studies
Large-scale 3D printing has moved from concept to reality in both manufacturing and construction. The IDEA project stands out as a milestone in industrial manufacturing. Eleven companies and four research institutes, including Siemens Energy and toolcraft AG, worked together to develop automated production lines for metal additive manufacturing. These lines produced high-end gas turbine components and precision parts. The project cut development and throughput times by about 50%. It also improved automation and reduced costs, showing that both large corporations and small businesses can use metal 3D printing for series production.
In construction, several projects highlight the effectiveness of 3D printing in complex builds. For example, a recent project used 350 layers of 3D-printed clay, taking 200 hours and consuming an average of 6 kilowatts of energy. This process almost eliminated typical construction waste.
|
Metric |
Outcome |
|---|---|
|
Number of layers |
350 layers of 3D-printed clay |
|
Printing time |
200 hours |
|
Energy consumption |
Average of 6 kilowatts |
|
Waste reduction |
Near total elimination |
Note: Sovol SV08 Max, with its large build volume and material compatibility, enables similar achievements in educational and industrial settings, supporting rapid prototyping and functional part production.
Leading Projects
Several international and domestic projects have advanced the role of 3D printing in construction. In Japan, Serendix uses concrete 3D printing to produce up to 50 homes per printer each year. The company plans to scale up to 850 houses with 12 printers, improving operational efficiency. In China, a company built a large mansion in just 45 days using a single 3D printer. Dubai’s 3D printing projects reduced labor costs by up to 80% and construction waste by 60%. The world’s largest 3D printed building in Dubai cost 2.5 times less than traditional methods and required only half the workforce.
In the United States, Texas’ Community First! Village constructed a 3D printed Welcome Center and homes for the homeless at $4,000 per unit, with each build taking less than 24 hours. Ukraine rebuilt a school in a war zone using 3d printing in construction, completing the project in 40 hours. California used 3D printed fire-resistant homes to rebuild after wildfires, achieving 11% cost savings.
Major tire manufacturers such as Michelin, Goodyear, and Bridgestone have also adopted 3D printing in manufacturing. Michelin introduced a 3D printed tire in 2017, aiming for sustainable materials by 2050. Goodyear invested in a $77 million plant using 3D printing and tested airless tires on electric vehicles. Bridgestone uses 3D printing for tire molds, improving traction and reducing prototyping time.
These examples show how big 3D printers and advanced models like Sovol SV08 Max drive innovation in both manufacturing and construction. They help companies reduce costs, speed up production, and create sustainable solutions for global challenges.
Challenges and Trends
Material Limits
Large-scale 3D printing in construction faces several material challenges. Many technical reports highlight the following issues:
- Mechanical properties of 3D-printed composites, metals, and polymers often show inconsistent results.
- Failure rates in FDM printing can reach 41.1%, with human error causing over 25% of failures.
- Warping and layer shifts reduce the strength of large prints, sometimes to only 42% of smaller prints.
- Carbon fiber additives help limit thermal expansion and improve print quality.
- Post-processing, such as support removal and surface finishing, remains time-consuming and can increase breakage rates.
- Research gaps include the need for more testing, better parameter reporting, and sustainable material development.
Sovol SV08 Max addresses some of these issues with its large build volume and material compatibility, but the industry still seeks consistent mechanical performance and optimized printing parameters. Material waste remains a concern, although single-piece prints help reduce it.
Regulations
Regulatory compliance presents another major challenge for 3D printing in construction. International standards like ISO13485 and ISO10993, along with ISO Technical Committee 261 and ASTM Committee F42, guide the industry. Product liability laws, such as the EU Product Liability Directive, create complex requirements for all actors in the production chain. The decentralized nature of 3D printing complicates the definition of "manufacturer" and the legal status of CAD files. Rapid customization in construction introduces unique regulatory hurdles in design, biocompatibility, and quality control. The industry needs further guidance to ensure safe and consistent production as 3D printing in construction evolves.
Future Directions
The future of large-scale 3D printing in construction looks promising. Industry trends point to:
- Multi-material printers that integrate electrical, plumbing, and HVAC systems.
- Expansion into extraterrestrial construction, such as habitats on Mars or the Moon.
- Roadmaps focusing on printer efficiency, material diversity, and building code compliance.
- Market growth with a projected CAGR of 17% to over 80% in construction sectors.
- Advanced automation and AI-driven quality assurance for faster, more reliable production.
|
Category |
Challenges |
Future Trends and Innovations |
|---|---|---|
|
Production Speed and Scale |
Slow build times, cost-ineffectiveness for high-volume production |
High-speed printing, large-scale advancements |
|
Design and Engineering |
Need for new design principles, complex file preparation |
AI-driven generative design, process optimization |
|
Regulatory and Certification |
Ongoing standards development, complex certification, IP protection |
Secure digital solutions, standardization efforts |
|
Material Limitations |
Mechanical property gaps, multi-material challenges, high material costs |
Advanced materials, material science advancements |
The future outlook for construction includes more durable materials, standardized regulations, and a skilled workforce. Sovol SV08 Max and similar machines will drive innovation, helping the industry move from niche applications to mainstream adoption. As the construction sector embraces these changes, the future will bring safer, faster, and more sustainable building solutions.
Large-scale 3D printing now drives rapid change in manufacturing and construction. Companies see material waste drop from 50% to 7.5%, with cost reductions up to 50%. Automotive and aerospace leaders use this technology for lighter, safer parts. Healthcare providers like Mayo Clinic improve patient care with custom implants. Sovol SV08 Max shows how big 3D printers deliver speed and flexibility in construction. The construction sector benefits from faster project delivery, less waste, and safer sites. Market projections show the construction industry will see strong growth, reaching $5.2 billion by 2033. Overcoming current challenges will unlock more innovation and help businesses shape the future of construction. Leaders who invest in large-scale 3D printing today will set new standards for efficiency and sustainability in the future.
FAQ
What makes large-scale 3D printing important for manufacturing and construction?
Large-scale 3D printing creates big parts and structures quickly. Companies use it to save time, lower costs, and reduce waste. Builders print houses, bridges, and custom parts. This technology helps meet the demand for faster, more flexible production.
How does the Sovol SV08 Max stand out among big 3D printers?
The Sovol SV08 Max offers a 500×500×500 mm build volume. It prints at high speeds and supports many materials. Engineers and builders use it for large prototypes, furniture, and building components. Its reliability and versatility make it a top choice for professionals.
What are common applications of 3D printing in manufacturing?
Manufacturers use big 3D printers for rapid prototyping, custom parts, and small-batch production. Companies like Boeing and Michelin print tools, molds, and even end-use parts. This approach speeds up product development and supports on-demand manufacturing.
How does 3D printing in construction improve sustainability?
3D printing in construction reduces material waste and energy use. Builders use recycled materials and print only what they need. Projects like 3D-printed homes in Texas and Dubai show how this method lowers costs and supports eco-friendly building practices.
What challenges do companies face with large-scale 3D printing?
Companies face material limits, print failures, and regulatory hurdles. They must ensure strong, safe parts and meet building codes. Ongoing research and new machines like the Sovol SV08 Max help solve these problems and push the industry forward.
Tip: Staying updated on new materials and printer features helps companies get the most from large-scale 3D printing.