Want to stop stringing on your next print? You can do this by turning on retraction. You should lower the nozzle temperature. Try to make the printer move faster. Keep your filament dry. Clean the nozzle often. Stringing in 3D printing happens when melted filament leaks out while the printer moves. If you change your 3D print settings a little, you will see a big change. Here are the best ways to fix it:
- Turn on and adjust retraction.
- Lower nozzle temperature by 5-10°C.
- Make travel speed faster.
|
Common Cause |
Easy Fix |
|---|---|
|
Wrong retraction settings |
Make retraction distance and speed higher |
|
Nozzle is too hot |
Lower by 5-10°C |
|
Filament is wet |
Keep dry; dry at 50°C for 2-3 hours |
You do not have to be an expert. These tips help beginners and anyone who wants a cleaner print.
Key Takeaways
- Turn on retraction settings and change them to pull filament back when moving. This helps stop leaks.
- Make the nozzle temperature lower by 5 to 10°C. This keeps the filament hard and stops it from oozing.
- Make the travel speed faster. This means the filament is in heat for less time. It helps stop stringing.
- Keep filament dry. Pick good brands to stop problems from moisture.
- Clean the nozzle often or get a new one. This helps the filament move well and makes prints better.
Causes of Stringing in 3D Printing
Why Stringing Happens
You may see thin, hair-like plastic between print parts. This is called stringing in 3D printing. It happens when melted filament leaks out as the printer moves. If the nozzle is too hot, the filament gets runny and leaks more. The printer needs to cool the filament, but high heat makes this hard. Sometimes, you find blobs or extra bits on your print. These blobs come from oozing, which is another kind of stringing.
Tip: To stop stringing, check your printer’s temperature and retraction settings before printing.
Here are some reasons for stringing and oozing:
- Retraction settings are too low, so not enough filament is pulled back.
- Nozzle temperature is too high, so the filament drips out.
- Filament has moisture, which causes bubbles and messy prints.
Common Mistakes
Many beginners make the same mistakes when trying to fix stringing. You might forget to change slicer settings or store filament the right way. Here are some common errors:
|
User Error Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Retraction Settings |
Not enough retraction can cause stringing. |
|
Temperature Adjustments |
|
|
Filament Handling |
Wet filament creates bubbles and more stringing. |
You can fix these mistakes with small changes. Try raising retraction distance by 1 mm or speed by 5 mm/s in your slicer. Lower the print temperature by 5°C. Store filament in a dry box to keep it dry. If you see bubbles or strings, check if your filament is dry. Moisture makes bubbles during printing, which causes more stringing in 3D printing.
Note: Turning off vertical lift (Z-Hop) and setting wipe distance to 0.4 mm or more can help stop stringing and oozing.
If you use these tips, your prints will look cleaner and have fewer strings. Small changes help both new and experienced users.
Printer Settings to Reduce Stringing and Oozing
Getting rid of 3d printer stringing starts with dialing in your slicer settings. You can make a big difference by adjusting retraction, temperature, and travel speed. Let’s walk through each step so you can prevent stringing and get cleaner prints.
Retraction Settings
Retraction settings are the first thing you should check when you see stringing in 3d printing. Retraction pulls the filament back into the nozzle during travel moves, stopping it from leaking out. You can change two main things: retraction distance and retraction speed.
Here’s a simple way to test what works best for your printer:
- Start with a retraction distance of 1mm and a travel speed of 150mm/s. You might still see some stringing.
- Increase the retraction distance to 2mm, keeping the travel speed at 150mm/s. You should notice fewer strings.
- Try 3mm retraction with 150mm/s travel speed. Most users find this setting eliminates stringing and oozing.
If you use PLA, PETG, or ABS, you may need to adjust these numbers. For most 1.75mm filaments, starting at 3mm works well. Some brands suggest going up to 5mm. Keep your retraction speed moderate, around 25mm/s, and test until you find what works for your setup. Changing retraction settings helps you prevent 3d print failures and gives you smoother results.
Tip: If you see blobs or strings after a print, try increasing retraction distance by 1mm or speed by 5mm/s in your slicer settings.
Nozzle Temperature
Print temperature plays a huge role in 3d printer stringing. If your nozzle gets too hot, the filament becomes runny and leaks out during travel moves. You can reduce stringing and oozing by lowering the temperature in small steps.
- For PETG, keep the nozzle temperature between 230°C and 250°C.
- Lower the print temperature by 5°C at a time to find the sweet spot.
- Printing closer to 230°C helps reduce stringing, while higher temperatures improve layer bonding.
Here’s a quick table to show how temperature changes affect your filament:
|
Temperature Change |
Filament Viscosity |
Stringing/Oozing |
Print Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
|
-5°C to -10°C |
Thicker |
Less |
Smoother |
|
+5°C |
Runny |
More |
Messier |
If you print at lower speeds, you can drop the temperature without hurting print quality. Always test a small part first to see how your filament reacts.
Travel Speed
Travel speed is another key slicer setting that helps you eliminate stringing. When you increase travel speed, the nozzle moves faster between print areas. This means the filament spends less time exposed to heat, so it’s less likely to ooze out.
Try these steps to find the best travel speed:
- Set travel speed to 150mm/s for non-print moves. You’ll see some improvement.
- Raise travel speed to 200mm/s. Most printers handle this well and you’ll notice fewer strings.
- Go up to 250mm/s if your printer can handle it. This usually stops 3d printer stringing completely.
When you boost travel speed, you give the filament less time to leak out. If you still see strings, combine higher travel speed with better retraction settings.
Note: If your printer starts to skip or make strange noises, lower the travel speed a bit. Not all printers can handle the highest speeds.
Slicer Tips
Your slicer software has special features to help you prevent stringing. You can use these settings to fine-tune your prints:
- Turn on retraction. This is the most important step to stop 3d printer stringing.
- Adjust retraction distance and speed. Longer distance can help, but don’t go too high or you might cause jams.
- Lower the print temperature in your slicer settings. Less heat means less oozing.
- Increase print speed for travel moves. This reduces the time the filament can leak out.
- Use “Combing” or “Avoid Crossing Perimeters” features. These options keep the nozzle inside printed areas during travel, so you get fewer strings.
- Try “Wipe” or “Coasting” settings. These features help clean the nozzle tip before moving, which can reduce stringing in 3d printing.
Here’s a step-by-step checklist for slicer adjustments:
- Enable and optimize retraction.
- Lower nozzle temperature by 5–10°C.
- Increase travel speed for non-print moves.
- Clean or replace the nozzle if you see leaks.
- Keep filament dry and store it in a sealed box.
Tip: Always test new slicer settings with a small print before starting a big project. This helps you catch problems early and avoid wasted filament.
If you follow these steps, you’ll see a big improvement in your prints. You can reduce stringing and oozing, prevent 3d print failures, and get smoother results. Small changes in slicer settings make a huge difference for both beginners and experienced users.
Filament and Maintenance for 3D Printer Stringing

Filament Quality and Type
You might not think much about the filament you use, but it plays a huge role in 3d printer stringing. Cheap or low-quality filament often has uneven thickness. When the diameter changes as it feeds into your printer, the flow of plastic becomes unpredictable. This can cause your printer to push out too much or too little material, which leads to stringing between parts. If you want to prevent stringing, always choose filament from a trusted brand. Look for spools that promise tight diameter tolerance. You can check the box or the product page for this information.
If you notice your prints have lots of strings, try switching to a different brand or type of filament. Some materials, like PETG, tend to string more than PLA. You may need to adjust your slicer settings or print temperature when you change filament types. Always run a small test print when you try a new spool. This helps you spot problems before you start a big project.
Tip: If you see sudden changes in print quality, check your filament for knots, bumps, or uneven spots. These can cause 3d printer stringing and even jams.
Moisture Control
Moisture is one of the biggest reasons you see 3d printer stringing. Filament absorbs water from the air, especially if you leave it out for a few days. Wet filament acts differently when heated. It creates more pressure inside the nozzle, which pushes out extra plastic during travel moves. This makes stringing worse and can even cause bubbles in your prints.
Here’s what happens when your filament gets wet:
- Moisture in filament is the leading cause of stringing issues in FDM printing.
- Wet filament changes flow behavior, increasing pressure in the nozzle.
- This pressure causes material to ooze out during retractions, leading to stringing.
- Proper drying of filament can significantly reduce stringing problems.
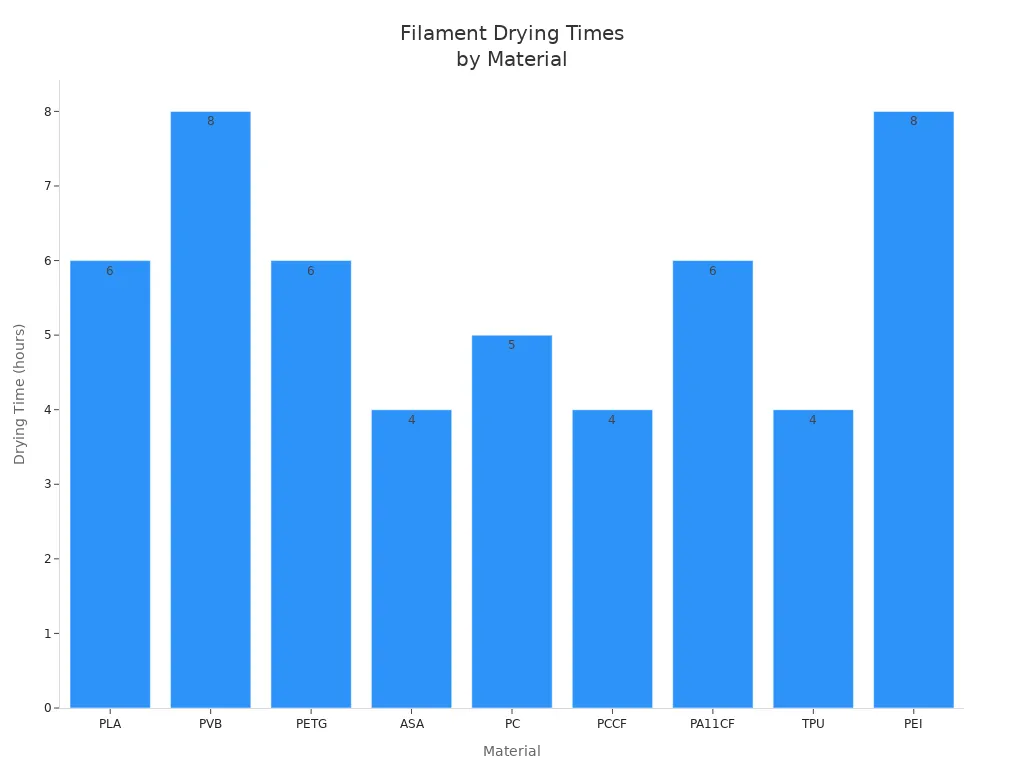
You can fix this by drying your filament before you print. Many people use a regular oven or a special filament dryer. The drying time and temperature depend on the material. Check out this table for the best settings:
|
Material |
Temperature |
Time |
|---|---|---|
|
PLA |
45 ºC |
6 hours |
|
PVB |
45 ºC |
8 hours |
|
PETG |
55 ºC |
6 hours |
|
ASA |
80 ºC |
4 hours |
|
PC |
85 ºC |
5 hours |
|
PCCF |
95 ºC |
4 hours |
|
PA11CF |
90 ºC |
6 hours |
|
TPU |
60 °C |
4 hours |
|
PEI |
150 °C |
8 hours |
You can dry filament at home by following these steps:
- Preheat your oven to 40°C to 50°C.
- Place the filament on a baking tray lined with parchment paper.
- Dry the filament for 4 to 6 hours, depending on the type.
- Watch the temperature to avoid melting the spool.
If you keep your filament dry, you will reduce stringing and oozing. Store your spools in a sealed box with silica gel packs. This simple habit helps you prevent 3d print failures and keeps your prints looking sharp.
Nozzle Cleaning
A clean nozzle is key if you want to eliminate stringing. Over time, small bits of old filament and dust can build up inside and outside the nozzle. This buildup blocks the smooth flow of plastic and causes extra oozing. You should check your nozzle often, especially if you print a lot or switch materials.
You can follow this simple cleaning schedule:
|
Frequency |
Task |
|---|---|
|
Daily |
Inspect nozzle and print bed for debris |
|
Weekly |
Clean print bed and check belt tension |
|
Bi-weekly |
Thorough nozzle cleaning and lubrication |
|
Quarterly |
Disassemble and clean the hot end thoroughly |
If you print for just a few hours each week, a quick check before each print and a deep clean once a month will work. If you use your printer every day, clean the nozzle every week.
Here are some easy ways to clean your nozzle:
- Heat the nozzle to 50-100°C. Use a brass wire brush to gently scrub away any plastic stuck to the outside. Wipe with a little alcohol to finish.
- For tough clogs, take off the nozzle and soak it in acetone or ethanol for a few hours. This dissolves stubborn residue.
Note: Regular nozzle cleaning helps you maintain print quality and avoid 3d printer stringing. It also keeps your printer running smoothly for longer.
If you use high-quality filament, keep it dry, and clean your nozzle often, you will see fewer strings and blobs. These simple steps help you get the best results from your printer. You will also spend less time fixing problems and more time enjoying your finished prints. Remember to check your print temperature and slicer settings when you change materials. Small changes can make a big difference in your 3d printer stringing results.
Design Tips to Eliminate Stringing
Model Adjustments
You can make smart changes to your 3D model and print setup to fight 3d printer stringing. When you design or slice your model, look for ways to cut down on travel moves. Fewer travel moves mean less chance for melted filament to ooze out and create strings. Try these features in your slicer settings:
|
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Only retract when crossing perimeters |
Stops retraction unless the nozzle crosses the outer edge, which helps hide oozing inside the part. |
|
Avoid crossing perimeters |
Plans travel paths to skip crossing outer edges, lowering stringing, especially on smaller printers. |
|
Prints one object at a time, so you get fewer strings between parts. |
|
|
Adjust Travel Speed |
Faster travel means less time for blobs to form. |
|
Minimize Long Movements |
Shorter moves over open spaces help prevent stringing. |
You can also change how you place your model and supports. Good orientation and support placement make a big difference. If you set up supports and rotate your model the right way, you use less material and get better print quality. This helps you avoid extra stringing and makes cleanup easier.
- Proper orientation and support structures improve print quality and reduce material waste.
- Smart design choices lower the need for post-processing and help you avoid 3d printer stringing.
If you want to try advanced anti-stringing techniques, start by tweaking these features in your slicer settings. You will see cleaner prints and spend less time removing strings.
Post-Processing (Heat Gun)
Sometimes, you still find tiny hairs on your finished print. You can fix this with a simple tool—a heat gun. Many users say a heat gun works well for removing stringing, especially on bigger parts. The heat gun softens the surface of materials like PLA or ABS. This melts away fine strings without hurting your print. Hold the heat gun a few inches from the part and use a low temperature. Move it slowly so you do not melt or warp the model.
Tip: Always test the heat gun on a small area first. You want to melt the strings, not the whole print!
If you follow these steps, you will get smooth results. You can use a heat gun for quick cleanup after printing. This trick saves you time and gives your project a professional look.
You can combine smart model adjustments and post-processing to tackle 3d printer stringing. Try these tips and see how much easier cleanup becomes.
You can stop stringing by following these top steps:
- Enable and optimize retraction.
- Lower nozzle temperature.
- Increase travel speed.
- Keep filament dry and use quality brands.
- Clean or replace the nozzle.
|
Setting |
How It Helps |
|---|---|
|
Retraction |
Pulls filament back, less ooze |
|
Temperature |
Keeps filament solid |
|
Travel Speed |
Less time for leaks |
Try small changes and keep your printer and filament in good shape. If stringing sticks around, revisit your settings and try drying filament or cleaning the nozzle. You’ll see smoother prints with just a few tweaks!
FAQ
What causes stringing even after I enable retraction?
You might still see stringing if your nozzle temperature is too high or your filament has absorbed moisture. Try lowering the temperature by 5°C and drying your filament. Clean your nozzle, too. These steps usually help.
How do I know if my filament is wet?
Wet filament pops or sizzles during printing. You may see bubbles or rough spots on your print. If you notice these signs, dry your filament in an oven or use a filament dryer.
Can stringing damage my 3D printer?
Stringing does not harm your printer. It only affects print quality. You can remove strings with a heat gun or by trimming them. Focus on adjusting your settings for better results next time.
What is the best travel speed to prevent stringing?
Most printers work well with travel speeds between 150mm/s and 200mm/s. Start at 150mm/s and increase if your printer handles it. Faster travel means less time for filament to ooze.
Do all filaments string the same way?
No, some filaments like PETG and TPU string more than PLA. Each material needs different settings. Always test new filament with a small print and adjust your slicer settings as needed.




















