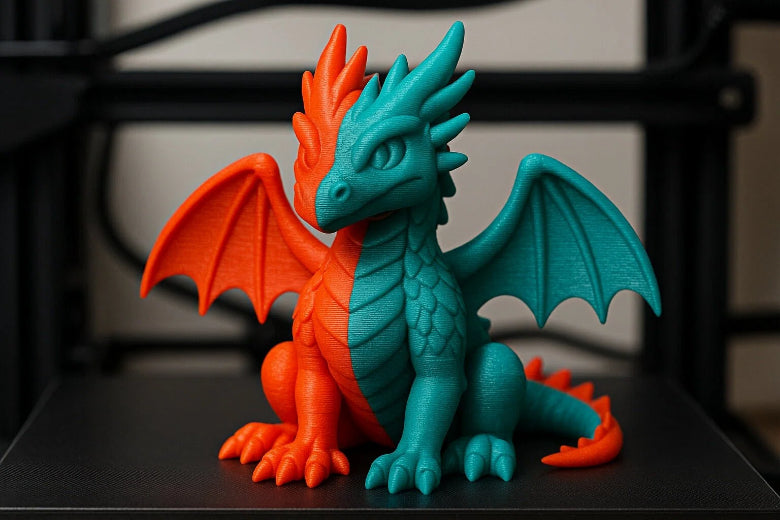
Multi-material 3D printing lets you make things with different materials in one print. You can mix rigid, flexible, or even conductive parts for cool results. This method does more than just add colors. The table below shows how multi-material and multi-color printing are different:
|
Method |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Filament Swapping |
You change the filament for color or material during a print. |
|
Dual Extrusion |
Two extruders print with different materials or colors in the same layer. |
|
Automated Material Switching |
The printer switches materials automatically for seamless multi-material printing. |
Multi-material printing is getting more popular. You can see it in healthcare and aerospace. It needs less post-processing and gives more useful parts. This helps both beginners and experts.
Key Takeaways
- Multi-material 3D printing lets you use different materials in one print. This helps you make things that are both strong and flexible. Using multi-material printing saves time. It also cuts down on extra work after printing. You can make complex designs without putting parts together. Dissolvable support materials help you print tricky shapes. They make sure your projects look neat and smooth. Trying out different material mixes can give you new ideas. For example, you can make soft grips on hard handles. Start with easy projects to see how materials work together. Then try harder prints as you learn more.
What Is Multi-Material 3D Printing
Printing Two or More Materials
Multi-material 3d printing lets you use different materials together. You can make objects with special features. For example, a part can be strong and also bend easily. Printing with more than one material saves time. You do not have to stop and change filaments.
Some printers have more than one hotend or use upgrade kits. Special systems help you print with many materials. Printers with IDEX can use two materials without mixing them. Devices like the Mosaic Palette or AMS join filaments before printing. These methods help you make cool designs and better parts.
- You can mix materials with different strengths.
- You can print things that need to bend and stay tough.
- Some kits let you use up to five filaments.
Tip: Try printing with two or more materials if you want a part that bends but stays strong.
Multi-Material vs. Multi-Color Printing
You might wonder how multi-color and multi-material printing are different. Multi-color printing uses the same material but in different colors. This is good for making bright models or toys. Multi-material 3d printing uses different types of materials, not just colors.
Here is a simple table to show the difference:
|
Feature |
Multi-Color Printing |
Multi-Material 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
|
Materials Used |
Same material, different colors |
Different materials, any color |
|
Main Purpose |
Visual appeal |
Functionality and performance |
|
Example |
Colorful figurines |
Soft-touch grips, rigid frames |
|
Printing Techniques |
Filament swapping, color mixing |
Dual extruders, AMS, MMU, IDEX |
With multi-material 3d printing, you can make a soft grip on a hard handle. You can also print parts with both flexible and stiff areas. You cannot do this with multi-color printing alone.
Key Benefits of Multi-Material Printing
Multi-material 3d printing gives you lots of benefits. You get more freedom to design and better quality parts. You can print shapes that are hard or impossible with one material.
- You can use support materials that dissolve, so tricky shapes are easier.
- You save time because you do not need to put parts together after printing.
- You do less work after printing, so it is easier for you.
Multi-material printing helps you make stronger and better objects. For example, you can print a part with a tough inside and a soft outside. This is helpful in cars and healthcare. You can also make test parts that look and feel like the real thing.
Note: Multi-material 3d printing can make your projects faster and easier. You do not need to glue or put together different parts.
You may have some problems, like getting materials to stick together. You might need to change the temperature for each material. Some printers use prime towers or ooze shields to keep prints clean when switching materials. These tools help you get good results.
Multi-material 3d printing lets you try new ideas and designs. You can make things that look nice and work well. You can also test new ways to build things.
How Multi-Material 3D Printing Works
Multi-material 3d printing uses smart ways to mix materials in one print. You can pick from single-nozzle switching, dual-nozzle or IDEX systems, and AMS/MMU systems. Each way works differently and has its own good points.
Single-Nozzle Switching
Single-nozzle switching uses one print head for many materials. The printer pulls in each filament one after the other.
- How it works: The printer stops, pulls out one filament, and puts in the next. It prints with each material one at a time.
- Pros: The hardware is simple and costs less. It is easy to upgrade.
- Cons: Changing materials takes longer. You might see some mixing at the switch.
- User level: This is good for beginners.
- Best for: It works well for simple multi-material 3d printing, basic test parts, and color changes.
Dual-Nozzle and IDEX Systems
Dual-nozzle printers have two print heads. IDEX systems let each head move by itself.
- How it works: Each nozzle prints a different material or color. IDEX lets both heads print at the same time or on different parts.
- Pros: Material changes are faster and there is less mixing. You get more freedom to design.
- Cons: The setup is harder and costs more. You need to adjust the printer carefully.
- User level: This is best for people with some experience.
- Best for: It is good for strong 3d parts, support materials, and prints that need clear lines between materials.
AMS/MMU and Multi-Input Systems
AMS and MMU systems feed many filaments into one nozzle.
- How it works: The system can switch between up to five filaments. It cuts and loads each one when needed.
- Pros: You can use many materials and do less work by hand. It is great for tricky designs.
- Cons: The system can jam and needs checking often. Prints can take longer.
- User level: This is for people with some skill.
- Best for: It works for multi-color 3d models, detailed test parts, and prints with lots of materials.
Material Feeding and Switching
You need to plan how the printer feeds and switches materials. Some printers use purge blocks or towers to clean the nozzle. This keeps your 3d prints neat and stops mixing.
- Different materials cool and shrink in their own way. Try small prints first to see what happens.
- Use your slicer software to pick which material prints where.
Temperature and Compatibility
Each material melts at a different temperature. You must set the right heat for each one.
|
Material |
Temperature Settings |
Cooling Strategies |
Support Structures |
|---|---|---|---|
|
PLA |
Varies |
Standard cooling |
Minimal supports |
|
ABS |
Higher |
Active cooling |
Extensive supports |
|
PETG |
Medium |
Moderate cooling |
Custom supports |
- Use temperature towers to find the best heat for both materials.
- Some materials do not stick together well. Try different mixes to see what works.
Tip: Always check your slicer settings before you start a multi-material 3d printing job. This helps you stop problems and get better prints.
Multi-material 3d printing lets you make strong, bendy, and colorful 3d objects. You can use these ways to make models with smooth surfaces, cool textures, and real uses.
Materials for Multi-Material Printing
Picking the right materials is very important for good 3d prints. You can mix different types to get special features. Let’s see some common choices.
PLA and PETG
PLA and PETG are used a lot in multi-material 3d printing. PLA is simple to print and looks smooth. PETG is stronger and can handle more heat. You might use PLA for most of the part and PETG for strong spots.
Here’s a quick chart about how they work together:
|
Material |
Compatibility Profile |
Performance Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
|
PLA |
Good for support, not for sticking forever |
Peels off PETG easily, smooth finish |
|
PETG |
Bonds well with ABS and ASA |
Sticks strong, not good for support |
You can make a 3d model with a PLA body and PETG clips. PLA comes off PETG easily, so it is good for supports.
Hard and Flexible Combinations
Mixing hard and flexible materials gives your 3d prints cool features. For example, you can use PLA or PETG for the main part and TPU for soft grips or hinges.
- Flexible materials like TPU bend and stretch without breaking.
- Hard and flexible mixes give both strength and comfort.
- You can make 3d parts with stiff frames and soft spots.
Try making a phone case with a hard shell and a soft edge. This mix keeps your device safe and feels nice to hold.
Engineering Materials
You can use special engineering materials for tough 3d projects. Materials like ABS, ASA, and PC are stronger and resist heat better. Nylon and carbon fiber blends make things even tougher.
PEEK and ULTEM are used in planes and hospitals. They can handle high heat and chemicals. CF-PEEK is a carbon fiber mix for really hard jobs. You can mix these with flexible filaments like TPU for custom parts.
Note: Engineering materials need hotter print settings. Make sure your 3d printer can get hot enough.
Support Materials
Support materials help you print tricky 3d shapes. Dissolvable supports like PVA or BVOH are easy to remove. You can print overhangs and bridges without breaking them.
- PVA melts in water and leaves a clean part.
- Supports do not hurt your part if you take them off carefully.
- Some 3d printers use breakaway supports for fast removal.
You can print a 3d model with PLA and PVA. After printing, put the part in water to remove the supports. This way, your 3d prints look neat.
Tip: Always check if your materials work together and need special heat before you start a multi-material 3d print.
Applications of Multi-Material Printing
Functional Parts
You can use multi-material printing to make strong and useful 3d parts. This method lets you combine hard and soft materials in one print. For example, you can print a box with a tough body and a flexible hinge. Many industries use this for real products.
Here is a table with common functional parts:
|
Functional Part |
Material Combination |
Application Examples |
|---|---|---|
|
Box Hinges |
PLA or PETG + TPU |
Enclosures, containers |
|
Anatomical Model Joints |
PLA or PETG + TPU |
Medical training, simulations |
|
Tool Handles |
PLA or PETG + TPU |
Firm grip, comfort |
|
Phone Holders |
PLA or PETG + TPU |
Non-slip, better usability |
|
Tweezers Tips |
PLA or PETG + TPU |
Precision grip |
You get parts that work better and last longer.
Aesthetic Prints
Multi-material 3d printing helps you make beautiful models. You can mix colors and textures in one 3d print. This is great for art, toys, and display pieces. You can use PLA for bright colors and PETG for a shiny look. Your prints will stand out and catch the eye.
Flexible and Rigid Parts
You can print objects that bend and stay strong. Mixing PLA with TPU lets you make parts that flex without breaking. This saves you time because you do not need to glue or assemble parts.
- You get more design options.
- You can make complex 3d objects with both stiff and soft areas.
- Your parts can act like real-world products.
This method works well for living hinges, grips, and snap-fit joints.
Prototypes and Complex Shapes
Multi-material printing lets you test ideas fast. You can print complex 3d shapes with support materials that dissolve in water. This makes it easy to create models with moving parts or tricky overhangs. You can use PLA for the main part and PVA for supports. Your prototypes will look and feel like finished products.
Wearables and Soft-Touch Parts
You can make comfortable and strong 3d wearables. For example, you can print a watch band with a tough inside and a soft outside. Tough epoxy gives durability, while soft elastic 30A adds comfort.
|
Material |
Properties |
Applications |
|---|---|---|
|
Tough Epoxy |
Durable, impact-resistant |
Robust wearable parts |
|
Soft Elastic 30A |
Flexible, soft, comfortable |
Ergonomic, soft-touch items |
Multi-material 3d printing helps you create custom-fit wearables and soft-touch grips for tools.
Tip: Start with simple projects like a phone holder or a soft-grip handle to learn how different materials work together.
Challenges and Solutions
Material Compatibility
You may face problems when mixing different materials in multi-material 3d printing. Some materials do not bond well. This can cause parts to crack or deform. Differences in shrinkage rates or strength can make layers pull apart. Chemical reactions between resins may also ruin your print. If one material cures faster or at a different temperature, you might see weak spots or poor fusion. Always check if your chosen materials work together before starting a 3d print.
Tip: Test small samples first to see if the materials stick and cure well.
Temperature and Warping
Temperature control is key for good 3d prints. If you use the wrong settings, parts can warp or lift from the bed. Each material needs its own heat level. For example, PLA prints well at 60-70°C, while ABS needs 100-120°C. Try these steps to reduce warping:
- Pick materials like PETG or nylon blends that resist warping.
- Use a heated build plate for better adhesion.
- Keep your print area warm with an enclosure.
- Apply glue stick, hairspray, or painter’s tape to help parts stick.
- Clean the build plate before each print.
Stringing and Switching Issues
Stringing happens when thin threads appear between parts of your 3d print. This is common in multi-material 3d printing because the printer switches filaments often. You can fix this by adjusting retraction settings. Retraction pulls the filament back during moves, stopping oozing. Set the right retraction distance and speed for each material. Cooling also matters. Fast cooling helps PLA, but ABS needs slower cooling to avoid cracks.
Print Time and Workflow
Multi-material 3d printing can take longer than single-material prints. Switching materials and building support structures add time. For large projects, print orientation can make a big difference. Changing the angle may cut hours off your print. You can also save money by planning your workflow and using the best print settings.
- Try different print angles to reduce time.
- Plan your prints to use less support material.
Clogging and Moisture
Moisture can ruin your filament and cause clogs in your 3d printer. Wet filament pops and bubbles during printing. You can prevent this by storing filament in airtight boxes. Use a dry box with a hygrometer and dehumidifier for best results. Keep the filament dry during printing by feeding it through a sealed container.
Note: Dry filament gives you smoother prints and fewer jams.
Multi-material 3d printing lets you make strong and flexible things. You can also make colorful 3d objects. Start with easy prints like phone holders. You can try soft-grip handles too. People who like hobbies use this method. Artists and engineers also find it helpful. Teachers can use it in class to show how mixing materials works.
Helpful resources for beginners:
- Guides show how to use two materials and different printers.
- Tips help you pick materials that work well together.
- Technical guides teach you how to make parts with special features.
|
Description |
|
|---|---|
|
Gradient Design |
You can blend materials smoothly for cool projects. |
|
Intuitive Interface |
You can choose materials easily without learning to code. |
The market for multi-material 3d printing is growing quickly. You can learn more and try new ideas as you get better.
FAQ
What is the difference between multi-material and dual-extrusion 3D printing?
Multi-material 3D printing lets you use more than one material in a single print. Dual-extrusion means your printer has two nozzles to print at once. You can use dual-extrusion for printing with two colors or two materials.
Can I use any filament for multi-material 3D printing?
Not all filaments work well together. Some do not stick or need different heat. Always check if your filaments match before you print.
Why do I need dissolvable support materials?
Dissolvable supports help you print tricky shapes. You can soak your print in water to remove them. This keeps your finished part neat and smooth.
How do I avoid stringing when switching materials?
You can fix stringing by changing retraction settings in your slicer. Try small test prints first. Clean the nozzle between switches for better results.
Is multi-material 3D printing good for beginners?
Yes! You can start with easy projects like phone holders or soft handles. Multi-material 3D printing helps you learn and make cool designs.