When I first stood in front of a wall of filament options, I felt overwhelmed. So many colors, materials, and brands stared back at me. I quickly realized that to choose the right filament, I needed to match the type, diameter, and properties to both my printer and my project goals. This careful selection process ensures strong, reliable prints every time.
Key Takeaways
- Always check your printer's compatibility with filament types and diameters before making a selection. This prevents feeding issues and ensures smooth printing.
- Consider the intended use of your printed object when choosing filament. Match the material's properties, like strength and flexibility, to your project needs.
- Start with PLA for easy printing, especially if you are a beginner. It offers low warping and works well with most printers.
- Store filament properly in airtight containers with desiccants to prevent moisture absorption. This helps maintain print quality and filament longevity.
- Experiment with different filament types like PETG or TPU for advanced projects. These materials offer unique properties that can enhance your prints.
Key Factors to Choose the Right Filament
Printer Compatibility
When I started 3D printing, I quickly learned that not every 3d printing filament works with every printer. The first thing I check is whether my printer supports the material I want to use. Some printers only handle basic filaments like PLA, while others can print with advanced materials such as ABS or flexible filaments. I always review my printer’s manual or manufacturer’s website to confirm compatibility.
Here is a table that summarizes the most common compatibility issues I have encountered:
|
Compatibility Issue |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Filament Diameter |
Printers require specific filament sizes (1.75 mm or 2.85 mm). Using the wrong size can cause feeding problems or even damage. |
|
Filament Type |
Some printers are designed for certain materials (like PLA or ABS). Using an unsupported type can lead to poor print quality. |
|
Temperature Requirements |
Certain filaments need specific temperature settings to print correctly, which affects adhesion and warping. |
|
Printer Features |
Some materials require special features, such as enclosed build spaces, to avoid warping. |
|
Extruder Type |
Flexible filaments often need a direct-drive extruder, which not all printers have. |
Tip: I always double-check my printer’s supported filament types and diameters before I choose the right filament for a new project.
Filament Diameter
Filament diameter plays a critical role in 3D printing. Most printers use either 1.75 mm or 2.85 mm filament. I make sure to match the filament diameter to my printer’s specifications. If I use the wrong size, I risk feeding issues or even damaging my printer. Consistent diameter ensures smooth extrusion and stable material flow, which leads to better print quality. For high-detail prints, I prefer 1.75 mm filament. When I need to print larger, more robust parts, I sometimes use thicker filament, but only if my printer supports it.
Project Application
When I choose a filament, I always consider what I want to create. The intended use of the printed part guides my material choice. For example, if I need a strong and durable object, I select a filament known for its strength. If I am making a decorative item, I might prioritize color or finish instead.
Here is a table that helps me decide which 3d printing filament to use based on my project needs:
|
Consideration |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Quality and Durability |
Different filaments offer varying strength and stiffness, which affects the final print’s quality. |
|
Temperature Requirements |
Some filaments, like PLA, need lower temperatures, while others, such as Nylon, require higher heat. |
|
Environmental Factors |
I consider heat resistance and moisture absorption for objects exposed to tough conditions. |
|
Compatibility with Printer |
I always ensure the filament matches my printer’s specs for the best results. |
|
Experimentation and Innovation |
Trying new materials can improve creativity and functionality in my prints. |
Note: When I want to choose the right filament, I think about what to know about filament for my specific project. This approach helps me avoid common mistakes and ensures my prints meet my expectations.
By focusing on printer compatibility, filament diameter, and the application of the printed object, I can confidently choose the right filament for any project. I always remind myself that the best results come from matching the right material to both my printer and my goals.
3D Printing Filament Types
Choosing the right 3d printing filament starts with understanding the most common types of filament available. Over the years, I have experimented with a wide range of materials, each offering unique properties and best-use scenarios. Let me break down the main categories and share when I reach for each one.
PLA and Its Benefits
I often recommend PLA as the starting point for anyone new to 3D printing. PLA stands out as the most popular 3d printing filament for several reasons:
- Easy to print with most desktop 3D printers due to its low melting temperature.
- Minimal warping and shrinkage, which means prints come out smooth and accurate.
- Made from renewable resources, so it is biodegradable under certain conditions.
- Available in a wide range of colors and finishes, making it perfect for decorative models and prototypes.
- Emits little to no odor during printing, which makes it safe for indoor use.
- Some PLA options are food-safe, so I use them for kitchenware prototypes.
When I need a reliable, hassle-free material for basic models, toys, or test prints, I always reach for PLA. For most users, PLA covers the majority of everyday printing needs. However, when I require more strength or special properties, I consider other types of filament.
ABS and PETG
As my projects became more demanding, I started using ABS and PETG. Both offer advantages over PLA, especially for functional parts.
|
Property |
ABS |
PETG |
|---|---|---|
|
42 MPa |
50 MPa |
|
|
Flexural Modulus |
2.4 GPa |
2.0 GPa |
|
Glass Transition Temp |
~105°C |
~80°C |
|
Recommended Use |
Functional parts, automotive components |
Medical devices, food packaging, outdoor signage |
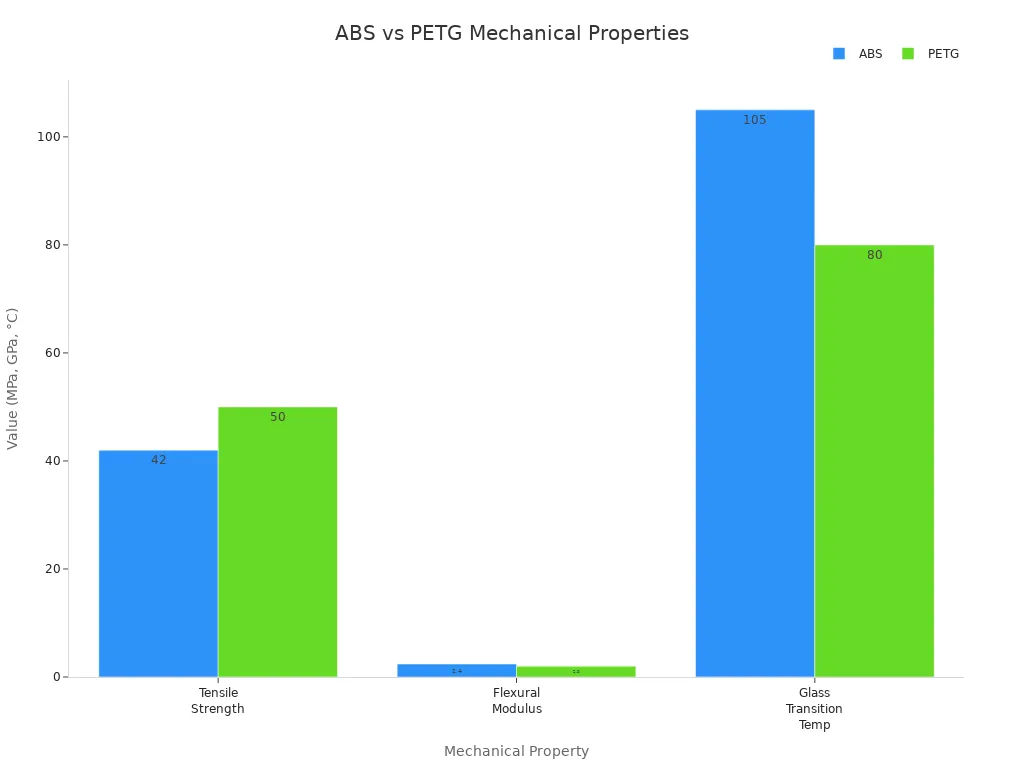
- ABS gives me strong, impact-resistant prints. I use it for mechanical parts and automotive components. It does require good ventilation because it can emit fumes during printing.
- PETG combines the ease of use of PLA with improved strength and chemical resistance. I rely on PETG for parts that need to withstand impact or exposure to moisture, such as outdoor signage and food-safe containers.
When I need a balance of strength, flexibility, and ease of printing, PETG is my go-to choice. For high-temperature or heavy-duty applications, I prefer ABS.
Flexible Filaments (TPU, TPE)
Some projects require flexibility and elasticity. That is when I turn to flexible filaments like TPU and TPE. These materials open up new possibilities for functional and ergonomic designs.
- TPU provides excellent elasticity and impact strength. I use it for functional prototypes and end-use parts that need to absorb shocks or handle dynamic forces.
- TPE is perfect for grips, flexible hinges, and shock-absorbing components in sports equipment and electronics.
- In protective gear, such as helmets, TPU cushions and absorbs impact, improving safety.
- I have used TPU in packaging lines to create bumpers that guide fragile products.
- In the fashion industry, TPU works well for custom insoles and flexible shoe parts, allowing for ergonomic testing.
- Automotive projects benefit from flexible filaments when I need tools that streamline assembly or create custom gaskets.
Tip: Printing with flexible filaments can be tricky. I always slow down the print speed and check if my printer supports direct-drive extrusion for the best results.
Specialty Filaments (PEEK, Others)
For advanced applications, I sometimes use specialty filaments like PEEK. These materials offer properties that standard filaments cannot match.
- PEEK delivers exceptional strength, chemical resistance, and heat tolerance. I have seen it used in aerospace components and medical implants.
- This high-performance, industrial-grade material requires very high printing temperatures. Most desktop printers cannot handle PEEK, so I only use it with specialized equipment.
- Specialty filaments like carbon fiber-filled materials and polycarbonate also provide unique benefits. Carbon fiber filaments give me lightweight yet stiff parts, ideal for structural components. Polycarbonate offers heat and impact resistance for industrial applications.
Standard filaments like PLA and ABS work well for most general-purpose 3D printing. When I need to meet extreme requirements, I turn to specialty filaments, but I always check if my printer can handle them.
Note: The world of 3d printing filament continues to grow. I stay updated on new types of filament to expand my creative and technical options.
Filament Properties Comparison
Strength and Durability
When I select a filament for functional parts, I always compare strength and durability first. Some materials stand out for their toughness and resistance to wear. For example, nylon works well for gears and sliding mechanisms because it absorbs impact and resists abrasion. PETG offers more strength than PLA and handles chemicals better, so I use it for mechanical parts and containers. Composite filaments, which include reinforcing fibers, give me maximum strength for industrial-grade applications.
|
Strength Characteristics |
Applications |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Nylon |
Excellent for gears and sliding mechanisms; absorbs moisture |
Gears, bushings, sliding parts |
|
PETG |
Stronger than PLA; good chemical resistance; easy to print |
Mechanical parts, containers |
|
TPU |
Flexible and impact-resistant; stretches without damage |
Gaskets, phone cases, dampeners |
|
Composite |
Maximum strength with reinforcing fibers; lightweight |
Industrial-grade applications |
Flexibility
Flexibility matters when I need parts that bend or stretch. TPU stands out because it stretches much more than PLA or ABS. I use TPU for gaskets, phone cases, and sports equipment. PLA feels hard and brittle, so it breaks under stress. ABS has moderate flexibility but cannot match TPU. I always match the flexibility of the filament to the needs of my project.
- TPU has much higher flexibility than PLA and ABS.
- TPU stretches without breaking, making it ideal for impact-resistant parts.
- I use TPU in footwear, sports gear, and medical devices.
- I choose the right material by thinking about the function of the finished part.
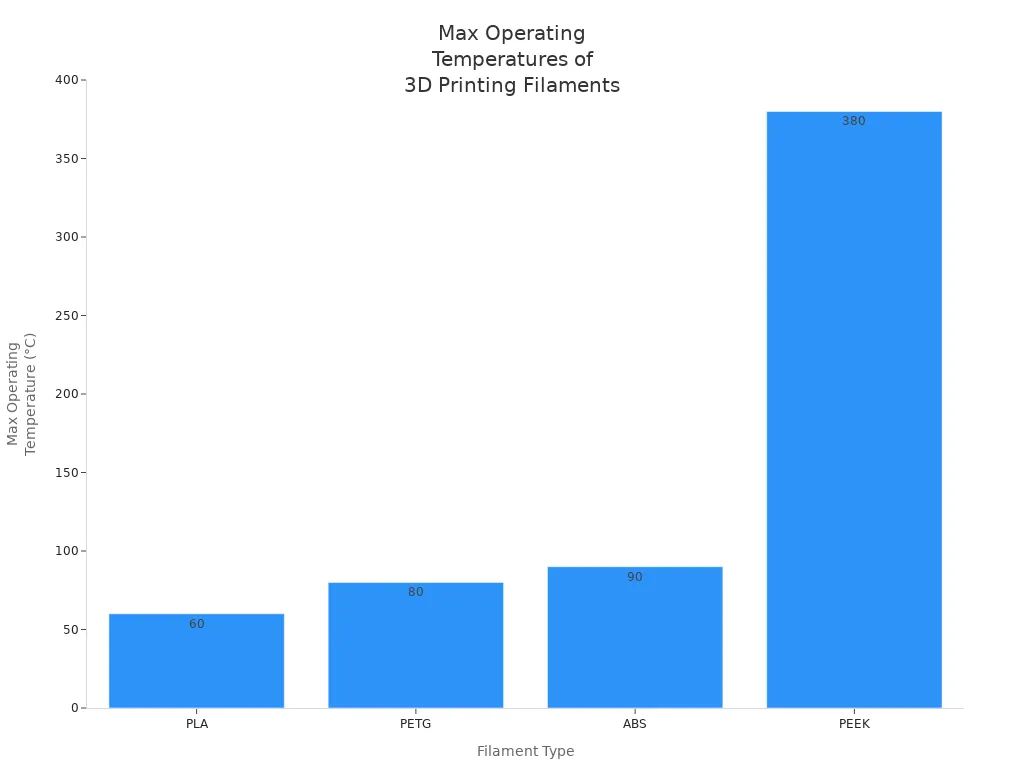
Temperature Resistance
I always check the temperature resistance of a filament before printing parts that will face heat. PLA works up to about 60°C, so I avoid it for hot environments. PETG handles up to 80°C, which covers many household uses. ABS resists temperatures above 90°C, making it suitable for automotive or outdoor parts. For extreme heat, I use PEEK, which can handle up to 400°C at the hotend and 150°C on the bed.
|
Filament |
|
|---|---|
|
PLA |
~60°C (bed) |
|
PETG |
~80°C (bed) |
|
ABS |
>90°C (bed) |
|
PEEK |
360-400°C (hotend) |
|
PEEK |
120-150°C (bed) |
Ease of Use
When I teach beginners about 3d printing filament, I always recommend PLA. PLA prints at lower temperatures, rarely warps, and does not need a heated bed. This makes it easy to use and gives predictable results. PETG also prints easily, but it needs a bit more care with temperature settings. ABS and PEEK require higher temperatures and special equipment, so I only use them when I need their advanced properties.
Tip: For your first prints, start with PLA. It helps you learn the basics without frustration.
Filament Selection Checklist
When I select a 3d printing filament, I follow a clear checklist to ensure the best results. This approach helps me avoid costly mistakes and keeps my prints consistent.
Match Filament to Printer Specs
I always start by verifying that the filament matches my printer’s requirements. I check the following specifications before making a purchase:
|
Specification |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Net weight |
|
|
Diameter |
+/- 0.05mm |
|
Print Temperature |
190-225°C |
|
Bed Temperature |
Not required, but 60°C recommended |
I confirm that my printer can reach the necessary temperatures and supports the filament diameter. This step prevents feeding issues and ensures smooth printing.
Align with Project Needs
I tailor my filament choice to the demands of each project. Here are the main criteria I consider:
- Physical properties: I assess heat resistance, chemical resistance, and transparency based on the object’s use.
- Ease of printing: For simple projects or when teaching beginners, I choose materials like PLA.
- Price and availability: I balance my budget with the performance I need.
- Printer compatibility: I double-check that my printer can handle the selected filament.
Tip: I always run a small test print to fine-tune settings and confirm the material suits my project.
Consider Storage and Safety
Proper storage keeps my filament in top condition. I follow these best practices:
- I store filament in sealed containers with desiccants to prevent moisture absorption.
- I use a hygrometer to monitor humidity and keep it below 20% RH.
- I avoid direct sunlight and store filament in a cool, dry place.
- I regularly inspect storage conditions and replace desiccants as needed.
Moisture can quickly degrade filament quality, especially for materials like ABS. By maintaining a stable environment, I ensure every print meets my standards.
Tips and Pitfalls
Common Mistakes
Over the years, I have seen many users make the same errors when working with 3d printing filament. One of the most common mistakes is ignoring the manufacturer's guidelines. I always read the instructions before loading a new filament. Another issue is using filament that has absorbed moisture. Wet filament leads to poor print quality and clogs. I also see people overlook what to watch out for when switching between materials. Failing to clean the nozzle or adjust temperature settings can ruin a print. I recommend keeping a checklist of what to watch out for before every print session.
Storage and Handling
Proper storage and handling keep my filament in top condition. I follow these best practices:
- I always adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations for storage.
- I keep the filament dry by using airtight containers or vacuum-sealed bags with desiccant packs.
- I avoid heat and direct sunlight, which can degrade the material.
- I maintain a clean, dust-free storage area to protect both the filament and my printer.
For extra protection, I use zip-lock bags with silica gel or invest in dry-storage boxes that control humidity. These steps help me avoid print failures and extend the life of my materials.
Sustainability
Sustainability matters in every project I complete. PLA stands out as the most environmentally friendly option because it is biodegradable and comes from renewable resources. PETG offers a good balance between recyclability and durability, but it does not break down naturally. ABS has a higher environmental impact due to its petroleum base and carbon emissions. I try to minimize waste, but I know that 89% of PLA 3d printing filament waste is not recycled globally. I always look for ways to reuse scraps and choose materials that align with my environmental goals.
When I choose the right filament, I follow these steps:
- Start with PLA for easy printing.
- Match the filament to my project’s needs, like strength or flexibility.
- Check my printer’s compatibility and temperature settings.
- Think about post-processing and my skill level.
|
Advice for Users |
Tip |
|---|---|
|
Beginners |
Use good quality PLA to learn the basics. |
|
Experienced Users |
Experiment with PETG or TPU for new projects. |
What is your favorite way to choose the right filament? Share your tips or questions below. For more guidance, explore resources on filament types and storage.
FAQ
What filament should I use for outdoor parts?
I choose PETG or ABS for outdoor prints. These materials resist UV light and moisture better than PLA. PETG works well for signs and containers. ABS handles higher temperatures. I avoid PLA outdoors because it deforms in heat and sunlight.
How do I prevent filament from absorbing moisture?
I store filament in airtight containers with desiccant packs. I check for signs of moisture, like popping sounds during printing. If filament absorbs water, I dry it in a filament dryer or a low-temperature oven.
Can I mix different filament brands?
I often use different brands, but I check the diameter and recommended print settings. Some brands have slight variations. I run a small test print first. This helps me avoid clogs or inconsistent extrusion.
What is the best filament for beginners?
I always recommend PLA for beginners. It prints easily, rarely warps, and works with most printers. PLA also comes in many colors. I use it for learning new techniques and testing printer settings.